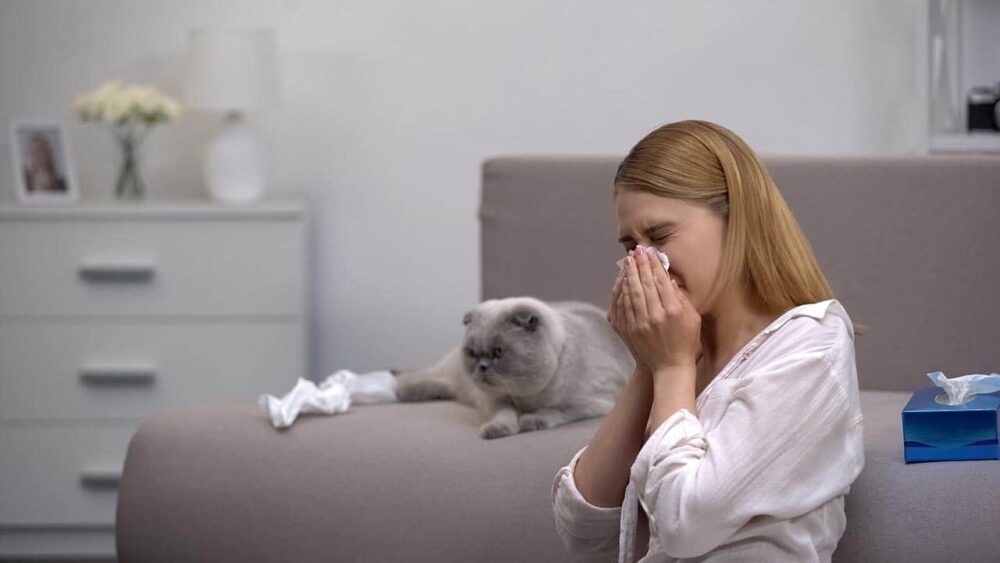
Approximately 10% to 20% of the population is allergic to cats and dogs. Of course, people can be allergic to far more than just pets. We can be allergic to different foods, pollen, dust, mold, etc. While everyone knows that humans experience allergies, fewer people know that pets do too.
Cats are often allergic to similar things as we are, namely fleas and foods, including beef, fish, chicken, dairy, and more. Naturally, far less research has been done on cat allergies than human allergies, so we don’t know nearly as much about what allergens affect cats.
Still, we know that humans can be allergic to cats. Does that work in reverse? Can cats be allergic to humans? It is hypothetically possible that, yes, cats can be allergic to humans in much the same way that people can be allergic to cats. However, to date, it isn’t a documented phenomenon.

Why Are Human Allergies Less Common Than Pet Allergies?
Most people probably never even consider the possibility of animals being allergic to people, even though many people are allergic to animals. Granted, it’s far less common for animals to be allergic to us than for us to be allergic to them. But why is that the case?
Well, for one thing, we do not have fur like many of the animals we are allergic to. It’s not that we are allergic to fur, though. People tend to be allergic to pet dander and saliva. Think of how many times you’ve watched your cat bathe itself with its tongue. Well, all of that saliva dries on its fur, leaving behind large amounts of the allergen found within saliva that causes people with cat allergies to react.
It’s not just your cat’s saliva, though, that’s to blame. Pet dander comes from their skin, and it also collects on your cat’s hair. When you touch your cat, all of the allergens from the dander and saliva are then catapulted into the air around, leaving airborne allergens everywhere. Soon, those allergens will settle on the floor and furniture, waiting for you to kick them up again.
As your cat sheds, they’re leaving behind allergens on every hair that comes off. This happens every time they stretch, move, and shake. We tend not to shed hair the way that cats do, so we’re not constantly ejecting allergens via hair into the atmosphere at the same rate as cats, dogs, and other furry mammals. And since we bathe so much more frequently than other furry mammal species, we don’t shed dead skin at the same rate either.

Other Things Your Cat Could Be Reacting To
While it’s rare for cats to have allergic reactions to humans, it’s less rare for them to have reactions to things we wear or use. For instance, that smelly soap you love to use in the shower is full of fragrances and perfumes that could cause a reaction in your cat. Even the laundry detergent you use has the same potential. Similarly, most cleaning products contain preservatives that can also cause reactions in cats.
Hypothetically (but not documented), cats can even be allergic to other pets. If you have multiple cats in the house, they could be allergic to each other’s dander and saliva. Likewise, your cat could be allergic to dogs in the same household or other animals that they come in contact with.
Conclusion
Though it is not documented for cats to be allergic to humans, it’s hypothetically possible. Though undocumented, a cat that is allergic to humans would presumably be managed in interesting ways with utmost care to our hygiene and perhaps some medication. But it’s well established and known that your cat may be allergic to something you’re wearing or using, such as your soap, shampoo, laundry detergent, or cleaners you use around the house.
- Related Read: Can Cats Detect Mold?
Featured Image Credit: Jupiter_79, Pixabay











