Click to Skip Ahead
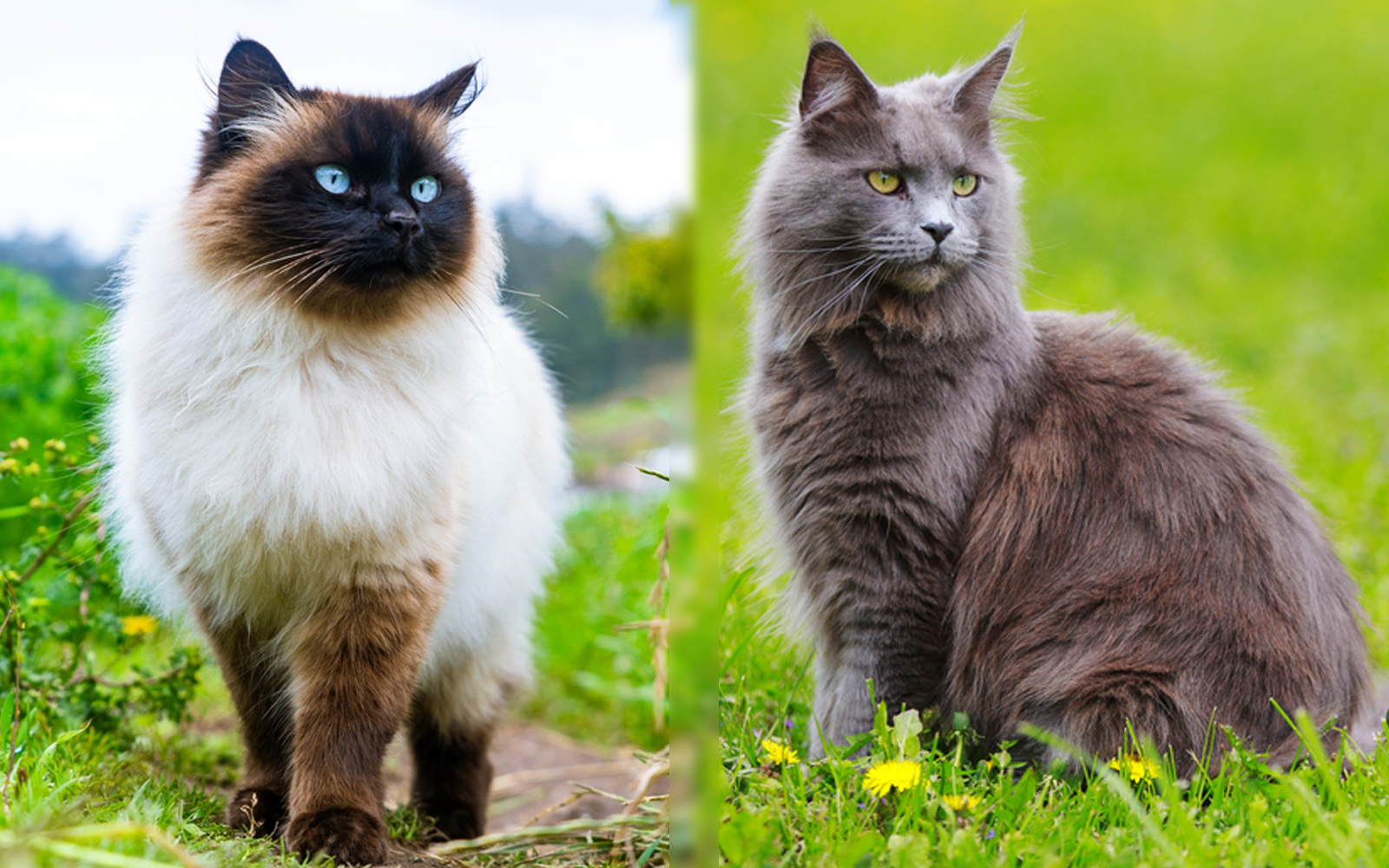
The British Shorthair and the Ragdoll are two popular and loved breeds. They also have a lot in common: they are stunning in appearance, large and stocky, and very loyal and affectionate.
But for all they have in common, they also have some key differences. These differences might be the make-it-or-break-it for your choice, so let’s get to know both cats—inside and out!
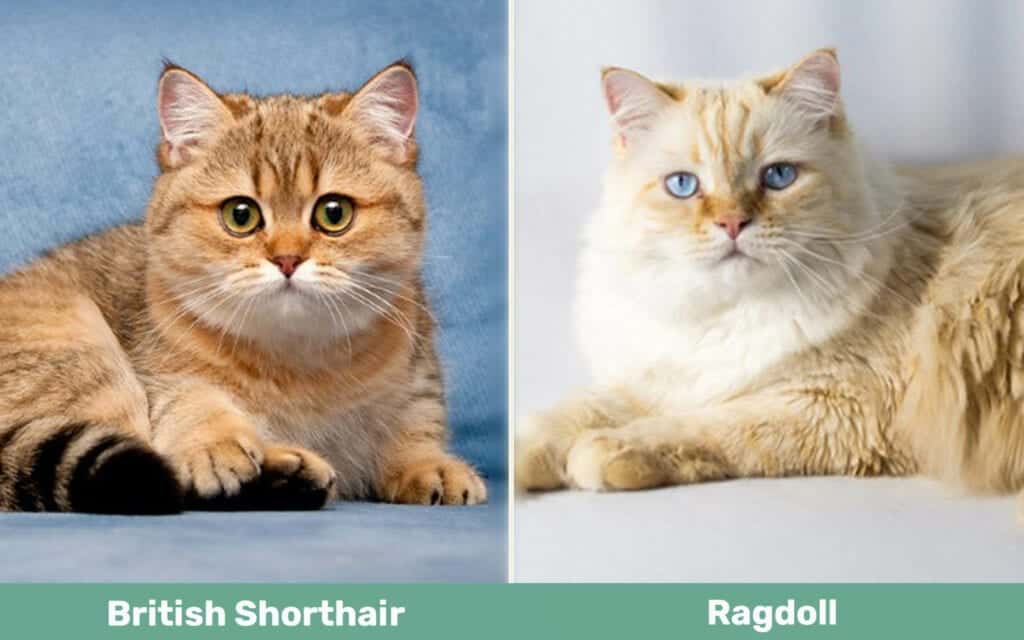
Visual Differences

At a Glance
- Average height (adult): 12–14 inches
- Average weight (adult): 8–17 pounds
- Lifespan: 12–20 years
- Energy level: Moderate
- Grooming needs: Low
- Shedding level: Normal/Seasonal
- Other pet-friendly: Yes
- Average height (adult): 12–25 inches
- Average weight (adult): 10–20 pounds
- Lifespan: 9–15 years
- Energy level: Low
- Grooming needs: Moderate
- Shedding level: Normal/Seasonal
- Other pet-friendly: Yes
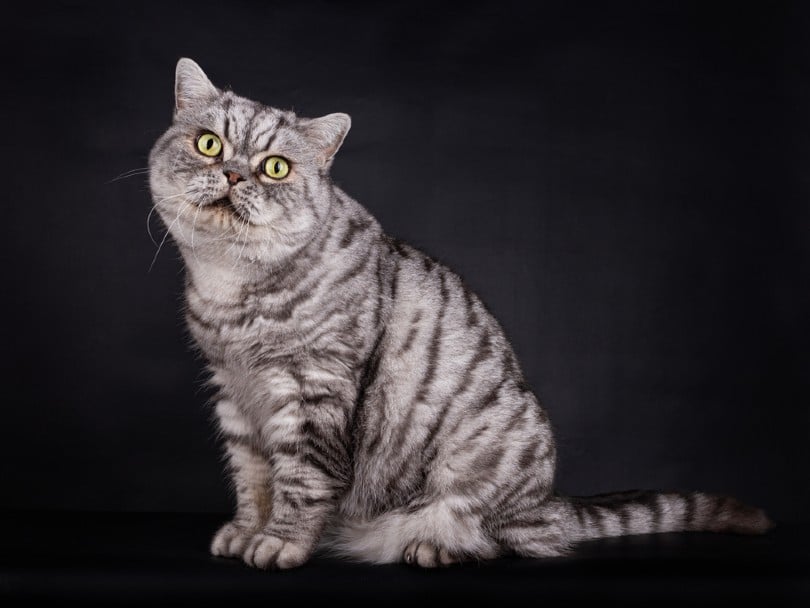
British Shorthair Overview

Personality / Character
The British Shorthair is a calm and confident breed. Their round faces and large orange eyes distinguish them from their American Shorthair cousins. Their plush coats, famously blue, also make them stand out from the pack.
Generally easy-going and affectionate, the British Shorthair is an intelligent breed. They were initially established in Great Britain to protect the food stocks of invading Romans from rodents. This does mean that they have a strong prey drive. However, their intelligence means they often get along with smaller animals in the home. They tend to be social and bond with other cats and dogs in the household.
Their social nature will mean they adapt well to a busy household, but they prefer not to be lap cats and instead coexist around the home. This independent streak persists in their disdain for getting picked up.
Grooming
While their soft coat is famous for being blue, they can come in many other colors and patterns. Whatever the color, the British Shorthair has a relatively low-maintenance coat. Short and soft, these cats can mostly take care of their grooming; however, a regular brush will not go amiss in assisting them. During seasonal shedding, brushing will also keep your home from being overrun with fluff bunnies of fur.
Baths are only necessary if your British Shorthair gets extra dirty or can no longer groom itself properly. They will also keep their nails trimmed with scratching, so be sure to provide them with plenty of scratchers to save your furniture.
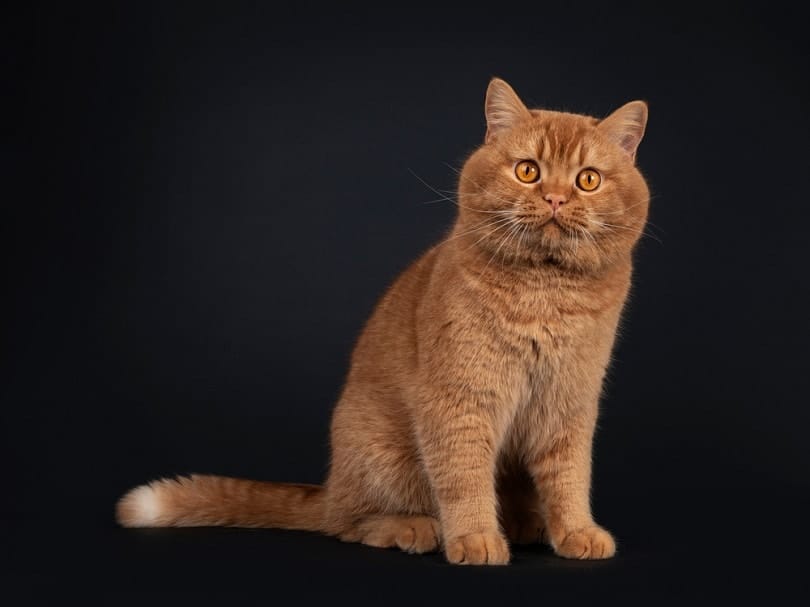

Health & Care
Despite being one of the oldest persisting cat breeds, the British Shorthair has a surprisingly healthy genetic makeup. They possess great vitality and an excellent lifespan. With few genetic worries, they are mostly at risk of the same things many other domestic cats are.
British Shorthairs may be at risk of inheriting a few genetic-specific disorders such as:
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Hemophilia
- Polycystic Kidney Disease
Many genetic issues can be detected with the breeders’ proper testing and screening of parent cats. Ensure you always research breeders you purchase from to ensure they follow all the safe and moral practices for cat health and welfare.
Suitable For:
Due to the relaxed nature of the British Shorthair, they make great additions to households of many different kinds. They will happily coexist with singles, couples, or families. They are reasonably good with kids but prefer not to be bothered during their “me” time, so ensuring they have safe spaces is essential.
British Shorthairs are rather independent, so they will suit you if you are looking for a partner in crime. However, they aren’t overly lovey-dovey, so they don’t enjoy being picked up, snuggling, or sitting on laps. They are great for those who want a low-maintenance companion.
Ragdoll Overview
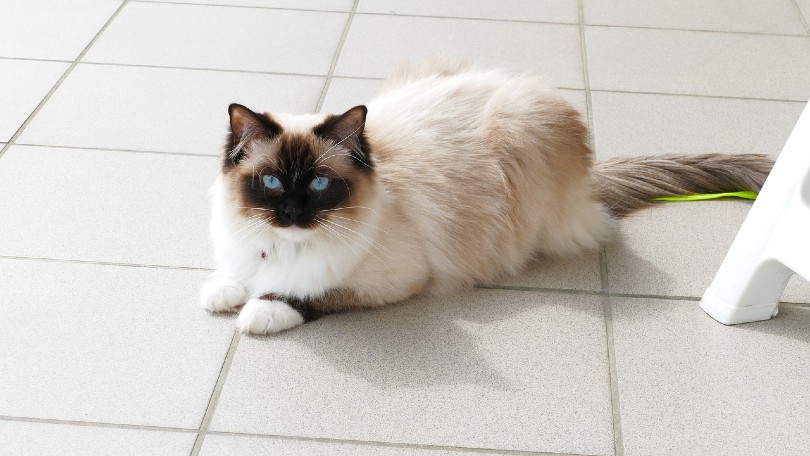

Personality / Character
Ragdolls are a truly unique breed, and all those who meet them seem to fall head over heels. They have a large stature, a fluffy coat, and piercing blue eyes. They seem to be the beauty queens of the cat world. However, they don’t let this go to their head and carry themselves with an extraordinarily relaxed nature, often quite goofy!
This breed received its namesake from its tendency to flop into your arms when picked up. They are happy and willing to be held and petted as often as you would like and often make their nightly bed right by their owner’s face.
This lovely nature makes them super friendly with humans, cats, and dogs alike. Ragdolls are also praised for their gentle nature around children, contrasting the usual short-fused cat. They can be a little too forgiving, though, finding themselves stuck in uncomfortable situations, unable to escape.
Grooming
The long luxurious coat of the Ragdoll looks like a real headache, right? But you’d be surprised how simple it is to care for and how little of a mess it makes. Unlike many other long-haired breeds, the Ragdoll coat is single-layered, lacking a dense undercoat. This means that grooming is a lot easier, and they shed only moderately, basically what you would expect from a domestic cat.
The coat is long and regular brushing is needed to keep it clean and smooth. Once a week will suffice, but daily would be ideal, particularly in the seasonal shedding seasons. The grooming requirements will increase as the Ragdoll ages. Elderly, sick, or disabled Ragdolls often struggle with their hygiene and need lots of attention. At this stage, professional grooming is recommended.
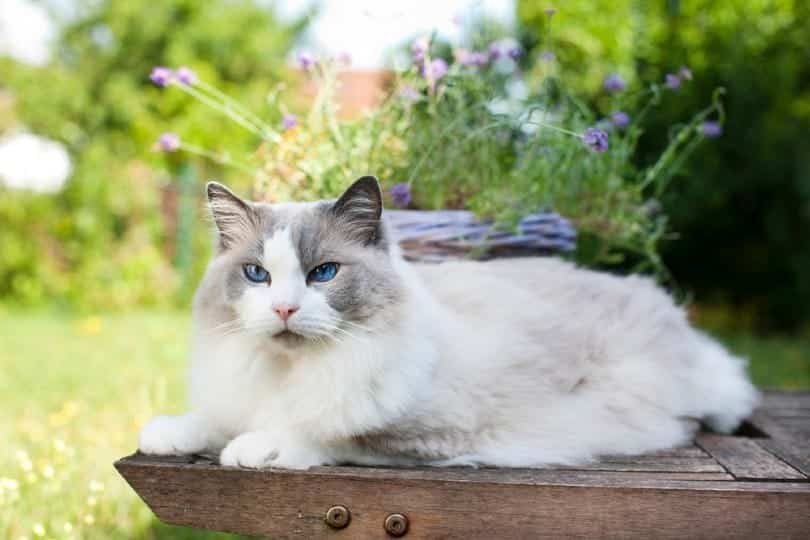

Health & Care
Ragdolls are a reasonably new breed to the cat scene, only being bred into existence in the 1960s. For this reason, they do not possess many genetic issues from hundreds of years of breeding. They are reasonably healthy in this department. Their large size also gives them a boost to their general health and resilience.
There are, of course, some genetic predispositions to be aware of for Ragdolls, including:
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Urinary tract infections
- Kidney disease
- Digestive problems
Again, breeders should be following ethical and moral codes to undergo the correct checks for genetic disorders for their breeding cats. Doing your research on your breeder will ensure you support good practice.
Suitable For:
The Ragdoll is a very affectionate breed. They bond very strongly with their family and don’t discriminate. For this reason, they are also great for anyone, from a single person to a large family.
This breed loves a lot of physical affection, so it is an excellent choice for those looking for a cuddle bug and bed warmer. If you enjoy a large lap cat and a fluffy spooner, then a Ragdoll will provide all this and more. Additionally, they are rather quiet in vocalizing, unlike other social cats like the Siamese.
Which Breed Is Right for You?
Ultimately, the British Shorthair and the Ragdoll are very popular breeds for great reasons. They are both beautiful, affectionate, and intelligent. And to top it off, they are both easy to care for and generally have good health.
At this point, you may still be finding it hard to choose! But it’s good to know there is no losing whether you get one or another, as both will bring lots of joy to your life. However, the critical difference is in their love languages.
The British Shorthair will adore you and be forever loyal, but they are not very tolerant of excess physical touch. You will be lucky if they want to sit on your lap, and they will tell you off if you try to pick them up. This independent nature is great for those who want a coexisting companion that is not very needy.
On the other hand, the Ragdoll is the opposite. Physical touch is how they give and receive love. For those looking for a lap cat and a cuddly pal, the Ragdoll may be more aligned for you. We also recommend both these cats for families with children, but the Ragdoll will likely be more tolerant of attempts of love from your toddler than the British Shorthair!
Featured Image Credit: Pixabay /Nynke van Holten, Shutterstock