Click to Skip Ahead
All pet parents are familiar with the common parasites, fleas, and ticks that can affect our four-legged friends, and they regularly prevent them with various medicines. However, there are several other parasites that can attach themselves to your pet, so what do you do if your pet is itching and scratching, you can’t find fleas or ticks, and your pet’s skin is looking really sore?

What Is Mange?
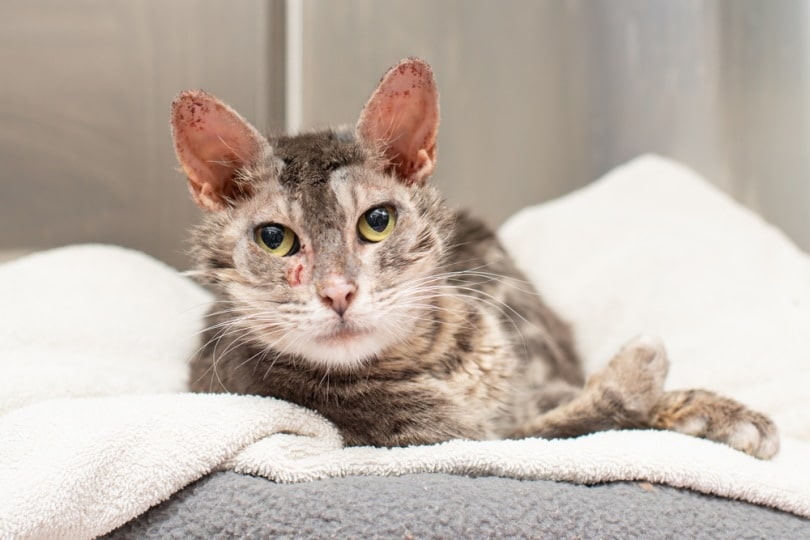
“Mange” is a term used to describe a group of contagious skin conditions in animals that cause redness on the skin, hair loss, and intense itching. It is often associated with stray animals and wildlife. But mange can affect any animal and can spread to people too.
So, you’re right to be concerned if you think your cat might have mange. However, it’s very rare in cats, and other skin conditions can cause similar signs, so let’s take a closer look at mange, and what to do if you think your feline friend is affected!
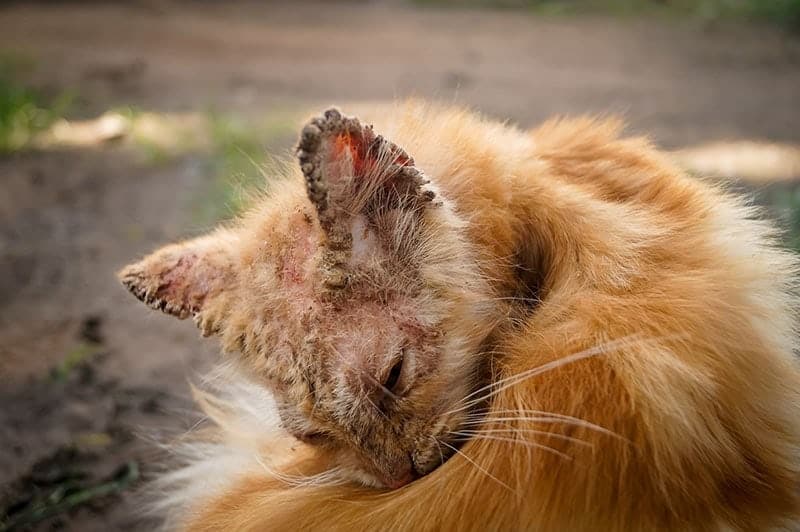

What Causes Mange?
Mange is caused by tiny parasites that can attach themselves to your pet and cause redness, flaky skin, intense itching, and hair loss. The mites are often picked up from wildlife or other animals that your pet comes into contact with when they are out and about. They burrow under or bite the skin and can be very uncomfortable for your pet.
“Mange” typically describes the signs and skin conditions that we see as a result of the mite infestation, but a few types of mites can cause mange.
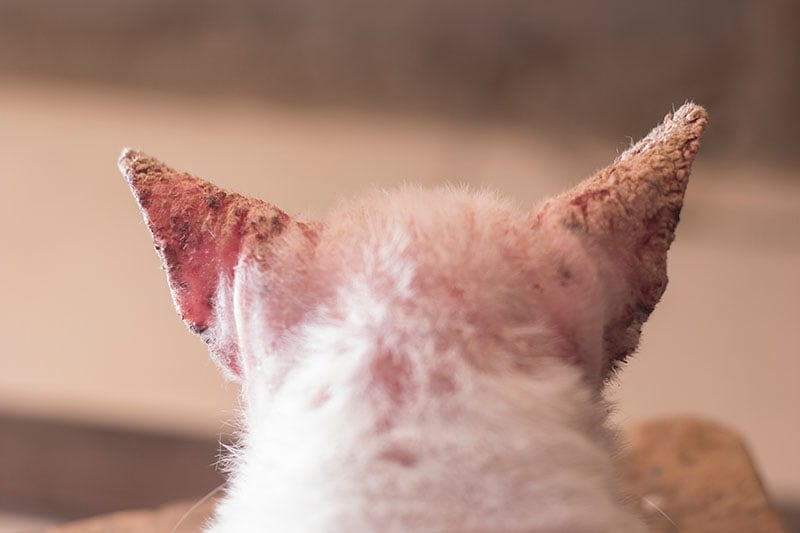

Types of Mange in Cats
- Canine Scabies – Caused by the highly contagious mite Sarcoptes scabei, this most commonly affects dogs, but direct contact can cause them to spread to cats.
- Feline Scabies – This is caused by the mite Notoedres cati, and it is a rare but highly contagious skin disease that affects cats. The mites look very similar to those causing canine scabies.
- Demodectic Mange (Demodicosis) – Demodicosis is caused by Demodex mites, which are ordinary residents on a cat’s skin. They don’t usually cause any harm to their hosts, but in cats with underlying health conditions or very young cats, they can cause problems.
- Trombiculosis (Harvest Mites) – Harvest mites are tiny red parasites that can attach themselves to cats in the late summer/early autumn (or harvest time, hence their name). The mites can easily be seen between your cat’s toes and are very itchy.
- Ear Mites (Otodectic mange) – Ear mites are tiny mites called Otodectes cynotis that infest the ear, causing irritation and inflammation, and are quite common in cats.
- Walking Dandruff (Cheyletiellosis) – “Walking dandruff” describes a condition where dandruff appears to move as the mites move around on the skin. It is caused by a mite called Cheyletiella and is highly contagious.
How Do Cats Catch Mange?
Mange is highly contagious, and to catch it, your cat needs to come into direct contact with another infected animal. Cats are avid hunters and spend much of their time outdoors, making them vulnerable to picking up mites and other parasites. This is the most common way cats catch mange, but they can catch it from direct contact with other infected cats and dogs.
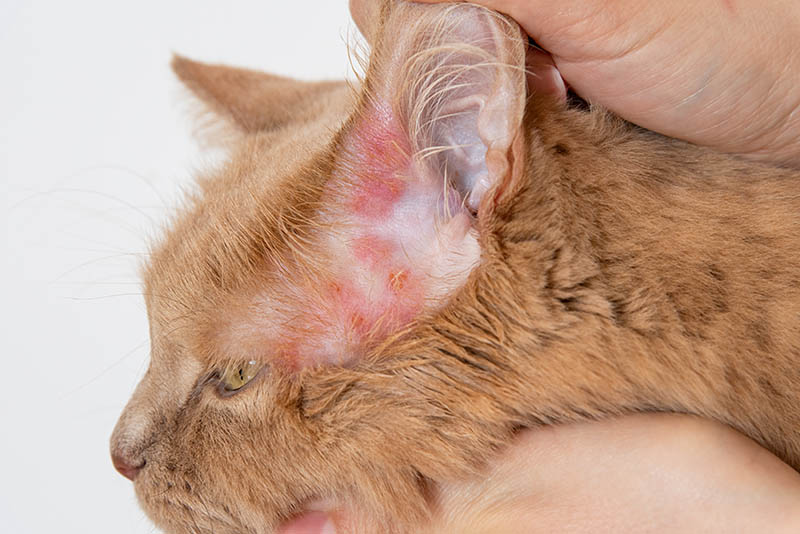
Skin conditions that look like mange
It might be easy to assume that your cat has mange if you’ve noticed the intense itching, hair loss, redness, and flaky skin. But before you get too worried, there are a few other skin conditions that can look very similar to mange.
Flea allergic dermatitis can cause similar signs like dry, itchy skin with hair loss, redness, and scabs. Some cats are allergic to flea saliva, which causes a skin reaction. Other contact allergies caused by anything in a cat’s environment could also cause similar signs.
It’s really important to get your cat checked by a veterinarian if you notice any changes in their skin, as most skin conditions are easy to diagnose with simple tests.
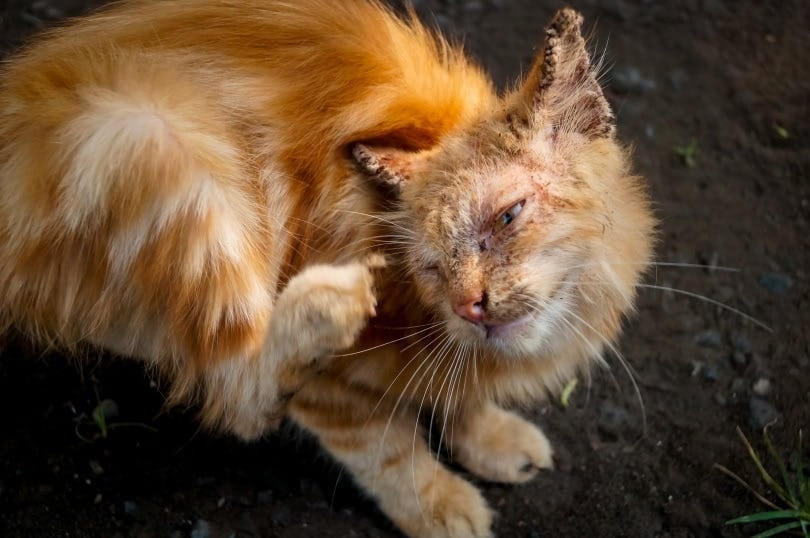

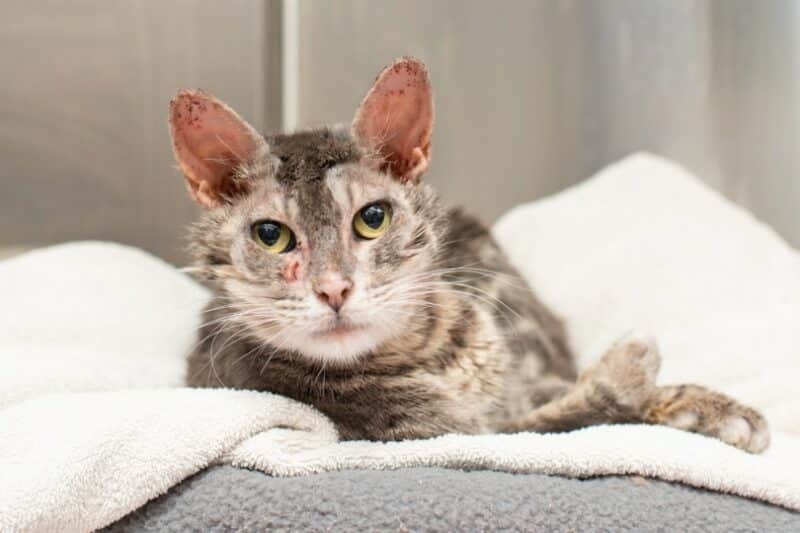
What Does Mange Look Like on a Cat?
Cats with mange will typically be very itchy, and you will notice your pet itching and scratching constantly. You might also notice restlessness and excessive grooming. The skin can have a greasy appearance and can become discolored. Sometimes, you may notice small bumps on the skin, as well as scabs and scaling.
Hair loss, redness, and swelling are also common. These signs are typically seen on the skin around the head, ears, and neck but can affect any part of the body. Mange can be diagnosed quickly and easily at the veterinary clinic by taking skin scrapes.
The veterinarian will look at them under a microscope, where it is easy to identify the type of mites. Sometimes, more tests are required, such as hair plucks or deep skin scrapes.
How Do You Get Rid of Mange on a Cat?
The good news is that it is straightforward to treat once mange is diagnosed and the mites identified. However, it can take 6 to 8 weeks for your cat to return to their usual self. Some treatments depend on the type of mites your cat has but can include topical formulas, tablets, or injections to kill the mites and their eggs.
They must be given regularly for several weeks and then maintained monthly to get on top of the infection. Special medicated shampoos can soothe and condition your cat’s skin. Your vet may also want to prescribe anti-itching medication and antibiotics to make your cat feel more comfortable if the damaged skin has become infected. You will also need to treat any other pets your cat has been in contact with.
You must keep your cat indoors and away from other animals until the mange has gone to prevent it from spreading. You should always wash your hands after handling your cat with mange, and ensure you wash all their bedding on a hot wash (140oF) to ensure the environment is clean. You should also vacuum thoroughly and wash any other soft furnishings that your cat likes to sleep on.
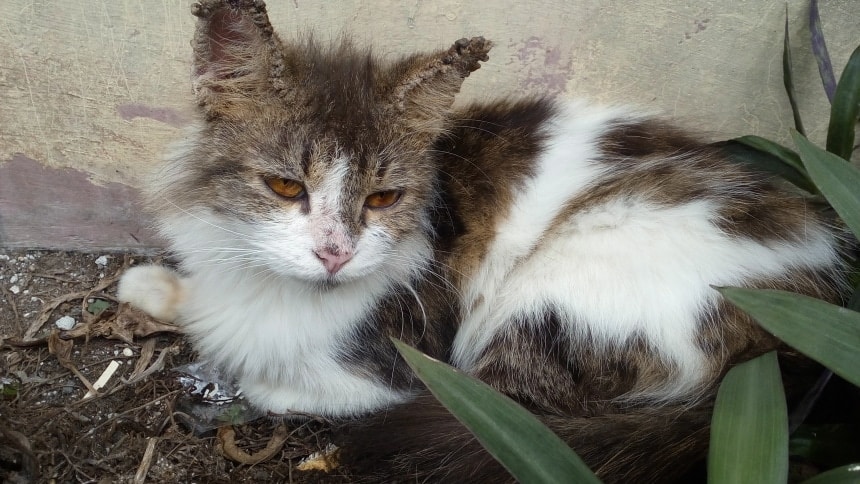

Preventing Your Pets From Catching and Spreading Mange
Prevention is critical when it comes to keeping your cat mite-free! A regular treatment with an effective parasite control treatment will give them good protection. This is especially important if your cat spends a lot of time outdoors or is an avid hunter. Several products are available in different forms, including spot-on treatments, tablets, sprays, and injections.
Many are prescription-only and cover a wider range of parasites, giving your cat ultimate protection. Speak to your veterinarian for advice on the best and most appropriate products for your pet.

Conclusion
Mange rarely affects cats; however, it can be an itchy and uncomfortable condition if your cat is unfortunate enough to catch it. There are different types of mange, and other skin conditions can look pretty similar, so if you are worried about your itchy cat, it’s best to get advice from your veterinarian. Once diagnosed, it’s easy to treat mange with a series of anti-parasite treatments, which you can also use in the long term to prevent any further problems.
Featured Image Credit by: Casey Elise Christopher, Shutterstock