In this article
If you’ve ever wondered if female cats have clitorises, the answer is yes; it’s an anatomical part shared by all female mammals! Fetuses all start with a structure called the genital tubercle that becomes a penis when exposed to fetal testosterone, but without it, the structures become clitorises.
While cats and humans share some anatomical structures, scientists caution against assuming that clitorises have the same function in all species. While the clitoris is largely linked to sexual pleasure in human females, little evidence suggests that it serves a similar function in female cats.

What Organs Are Part of the Male and Female Feline Reproductive Systems?
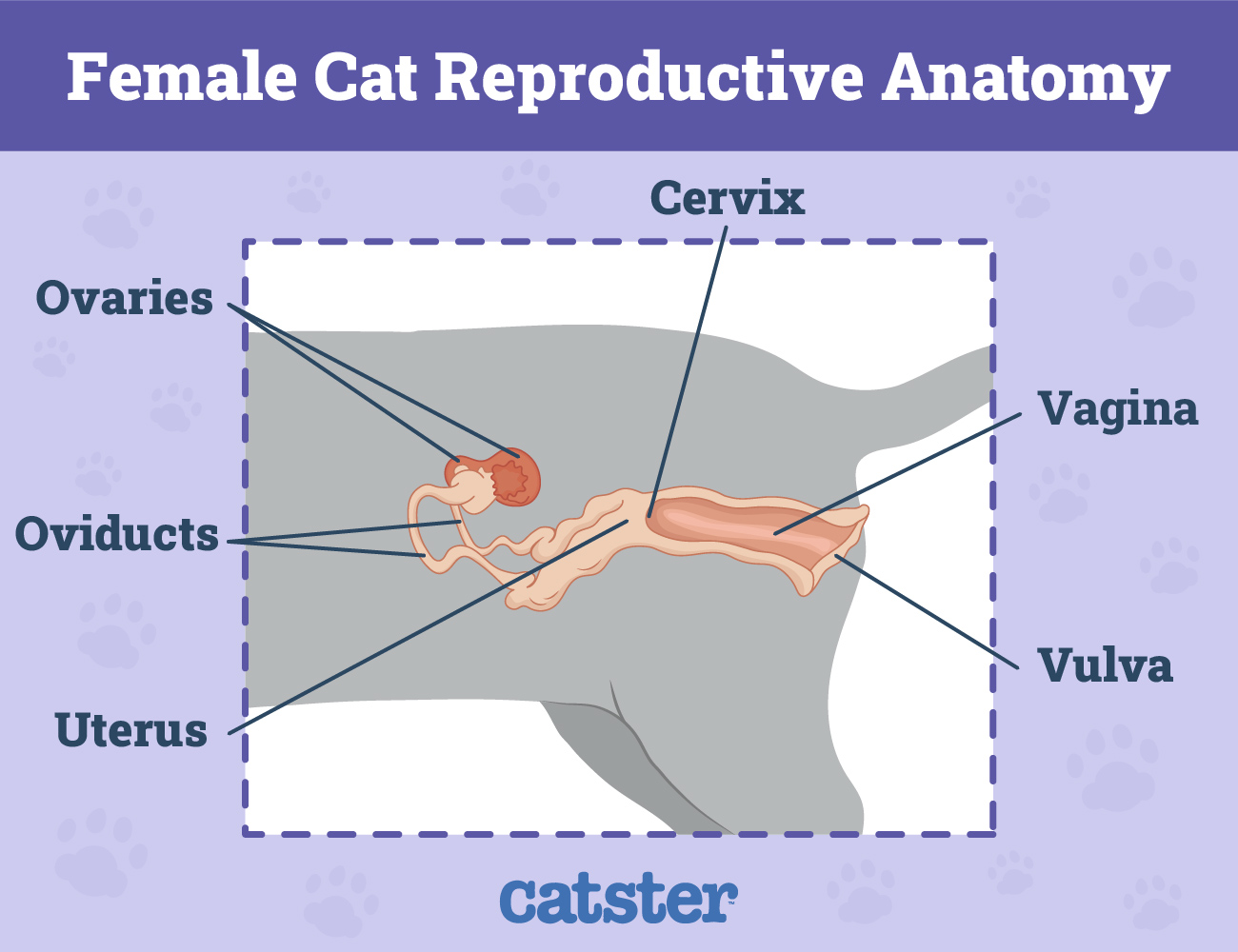
The female feline reproductive system consists of ovaries, fallopian tubes, which are also called oviducts, the uterus, cervix, vagina, and vulva. Feline ovaries release eggs, which are carried to the uterus via the fallopian tubes.
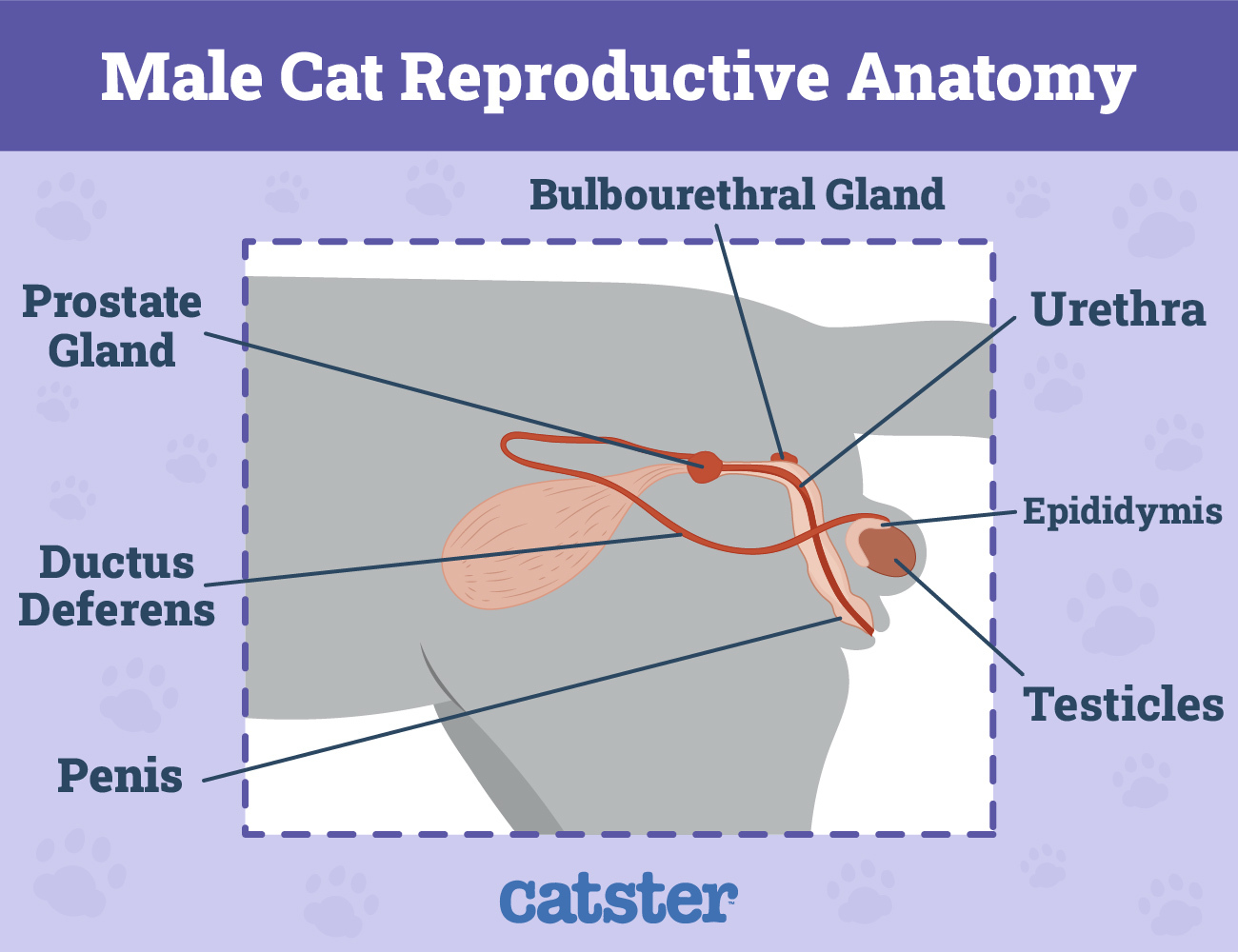
The cervix forms a barrier between the uterus and the vagina. It opens during childbirth and otherwise remains essentially closed to keep infectious agents at bay. In male cats, the epididymis stores sperm from the testes which then travels down the ductus deferens before it connects to the urethra.
How Does Feline Reproduction Work?
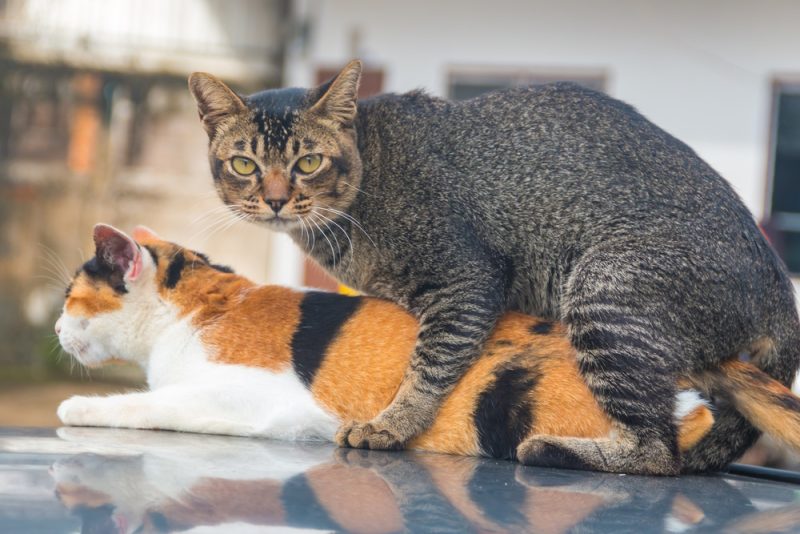
Cats are induced ovulators, and they only release eggs after having intercourse.
Most female cats need to have intercourse several times in a short period to induce ovulation. Cats are usually in active heat for about 1 week, but the cycle can repeat every few weeks, depending on the time of year.
Daylight actually has a significant impact on feline reproduction, and cats can only go into heat when exposed to between 14 and 16 hours of light. It’s one of the reasons so many kittens are born between January and October in locations above the equator.

How Long Do Feline Pregnancies Last?
Cat pregnancies generally last about 2 months, and queens can carry between 1 and 9 kittens at a time, but the average litter is closer to four. Cats don’t show many signs during the first 20 days of pregnancy (the first trimester), but many become more mellow and relaxed as time goes on.
Fetal heartbeats become detectable when queens are about 3 or 4 weeks along. Cats often start looking for an appropriate place to give birth during their third trimester.
Are Male Cats Involved in Kitten Rearing?
Most male cats don’t get involved in the day-to-day care of raising small kittens, and they’re essentially completely dependent on their mothers to provide food and warmth immediately after they arrive in the world.
Male domestic cats sometimes kill kittens, which is a behavior also commonly seen in male lions. Queens can mate with multiple male cats when in heat, and kittens in one litter can have different fathers, which is called superfecundation.
It’s why kittens from one litter can have different personalities and appearances. Fathers’ kitten-raising duties are also limited by the fact that many don’t live in the same household as their babies.


Conclusion
Female cats indeed have a clitoris, and all female mammals have them. The clitoris is formed from a structure called the genital tubercle, which becomes a penis when exposed to testosterone during fetal development. Without the presence of testosterone, the tubercle eventually becomes a clitoris.
Although the clitoris has a function linked to sexual pleasure in humans and some non-human primates, experts caution against assuming the structure serves a similar purpose in other species.
Featured Image Credit: Mary Swift, Shutterstock