While cats are generally well-behaved, sometimes their conduct can cause you to think,” My cat is a brat,” especially when there’s aggressive behavior involved. Aggression is vital in helping cats survive in the wild since it prevents them from being attacked by larger animals. Cats frequently become aggressive due to stress, anxiety, and fear, and it’s essential to identify what’s prompting your cat’s behavior so you can make a few adjustments to keep your buddy happy and calm.
Signs of an Aggressive Cat
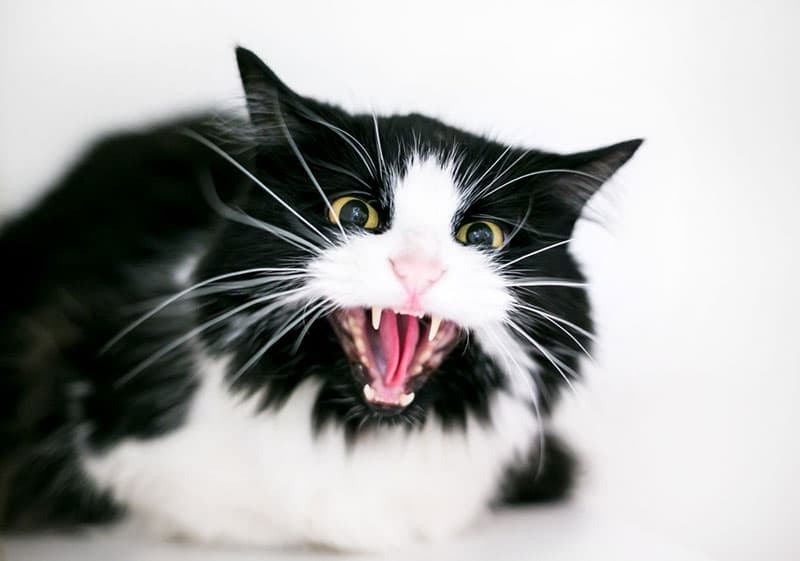
Cats typically use vocalization and body language to get their points across. Riled-up felines often have dilated pupils and flattened ears, and when cats are particularly irritated, their tails become puffed up. Vigorous tail thwacking can also indicate that a cat is on the verge of becoming aggressive.
Cats sometimes growl and hiss when scared or seriously aggravated, but growling is also seen in situations where cats wish to convey dominance. Scared cats can bite or scratch people and other animals when pushed and not allowed to go on their way; most cats attempt to hide or get away before things escalate.
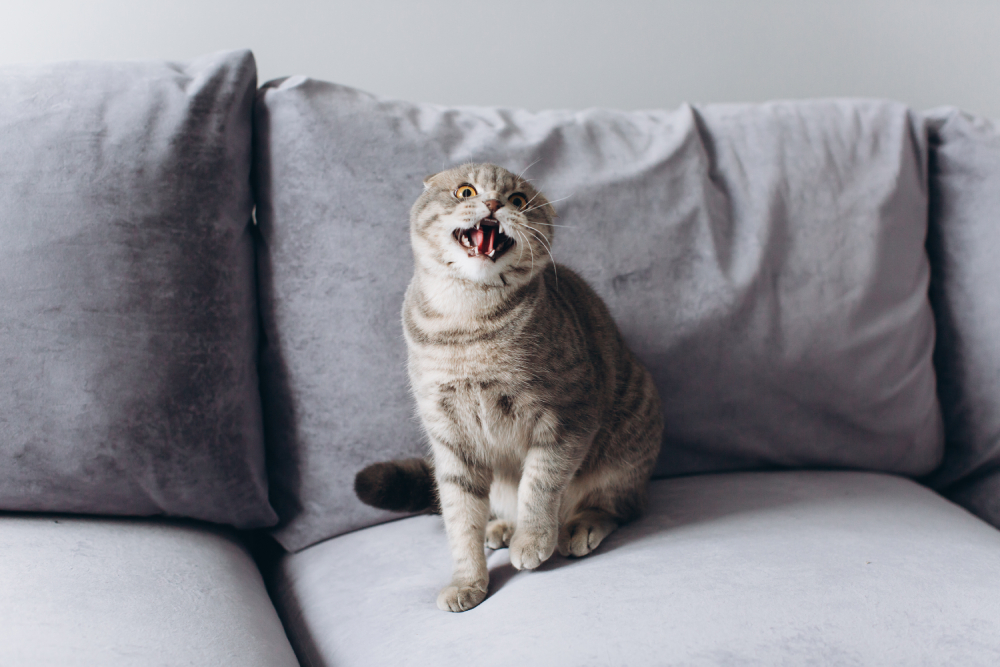

Are There Situations That Can Trigger Aggression?
A few situations are commonly linked to feline aggression, including fear, territoriality, unwelcomed petting, and when playtime becomes a bit too exciting.
1. Fear
Cats sometimes react fearfully when exposed to people, animals, or places they aren’t familiar with. Loud noises can also be a trigger. Cats can respond by scratching or hissing when someone they don’t know gets too close for comfort.
2. Territoriality
Aggression can result when cats’ territorial instincts are triggered, which sometimes happens when they have to adjust to the presence of a new animal or person in their domain. Some owners may think spoiled cat behavior contributes to their pet reacting negatively to a new roommate, but most cats aren’t fond of changes and take a while to adjust.
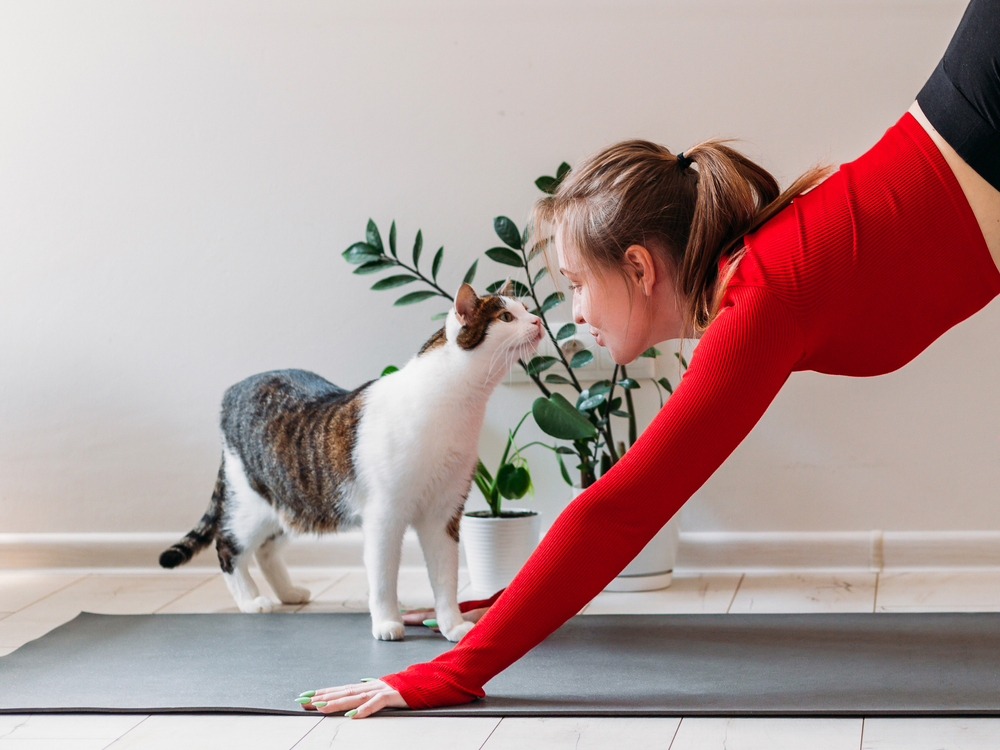
3. Petting
While cats enjoy being cuddled and petted, they sometimes want to be left alone and can grow tired of even the most enjoyable snuggles. Cats get irritated when petting goes on for too long, and they’re not allowed to go about their business peacefully.
They can also become annoyed if they don’t like the way or how they’re being touched and handled. Cats prefer being petted gently on their backs, shoulders, and heads; most don’t enjoy their tails and paws receiving human attention. They can also react sharply to friendly pokes and pats from small children.
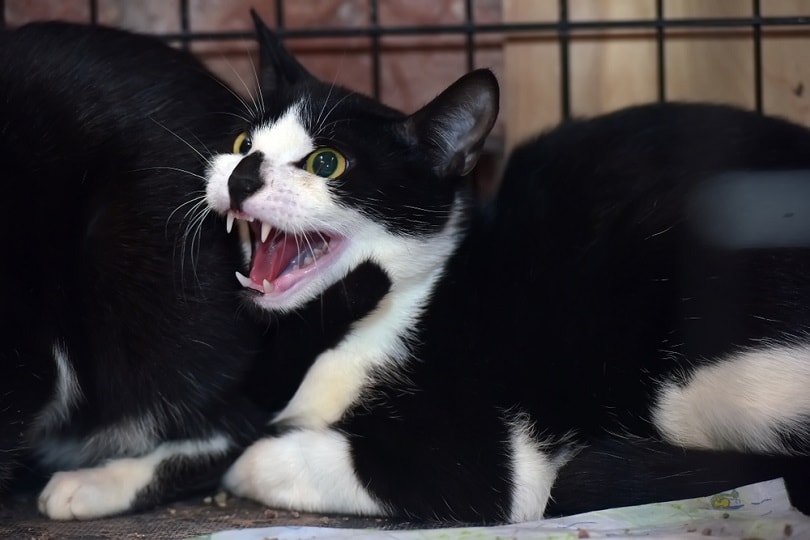

4. Play
Cats can get a bit carried away when they’re playing, which can result in conduct that crosses the line. Overenthusiastic play is most often seen in kittens and younger cats.
5. Resources
Tension can result in multi-cat homes when cats feel the need to compete for access to resources such as litter boxes, food and water bowls, toys, napping spots, and attention.
6. Pain
Dental pain, infections, and arthritis can all cause normally calm cats to become more aggressive. Cognitive decline and neurological issues can also be triggers of aggression.
7. Hormones
Unaltered male cats can be more aggressive than their neutered counterparts, and female cats can become less tolerant when they’re in heat.
Are There Ways to Encourage Slightly Mellower Feline Behavior?
Yes. Providing cats with private places to hang out, giving them toys to enjoy, and ensuring they get plenty of exercise are all great ways to support cats’ overall well-being. Veterinarians can provide guidance on medication and behavior modification techniques to help cats calm down. Spaying and neutering intact cats are often all that’s needed to address hormone-related aggression.

Private Space
Cats need comfortable spaces where they can get away from it all. A cardboard box with a blanket is more than enough to keep many cats who live alone happy, but those living in homes with other animals or small children benefit from having a quiet room where they have a place to nap, food to snack on, and toys to play with when in need of a time out.
Mental and Physical Stimulation
Ensuring that cats get enough play time to get rid of their spare energy can reduce their tendency to jump out and attack people walking by. Giving them toys and activities to enjoy and increasing their mental and physical stimulation helps decrease play-related aggression.
Multiple Resources
Providing at least one resource per cat plus an extra for good measure can reduce the tendency to battle over access to the basics. If you have two cats, it’s best to have three litter boxes to prevent conflicts, and you can increase the time you play with each to prevent your cats from competing for your affection.

Should I Be Concerned if My Cat Suddenly Starts Acting Aggressively?
Because behavioral changes are often the first signs of illness in cats, a veterinarian must see your cat if they suddenly start peeing outside the litter box, eating more or less, or behaving aggressively.
Conclusion
Aggression is a natural part of being a cat, but it’s less desirable when it leads to biting, chasing, and scratching. It can be caused by fear or stress, but you can reduce it by identifying what is bothering your cat. However, a health condition can also lead to aggressive tendencies, and you should talk to your veterinarian if your cat’s behavior suddenly changes.
Featured Image Credit: Mary Swift, Shutterstock