Is your cat constantly begging for food at night? Maybe it’s the early evening when you’re still awake, or perhaps you’re dead asleep and their meowing and pawing is waking you up. Either way, it’s beyond annoying.
Making it even more challenging is that you don’t know how to make it stop. Whether this is a new behavior or a persistent problem, there are things you can do to stop the issue. We’ve highlighted eight tips you can follow to help your cat stop begging for food at night so you can finally get a good night’s sleep.
The 8 Tips to Get My Cat to Stop Begging for Food at Night
1. Go to the Vet
If your cat didn’t use to beg at night and it’s a newer behavior, we highly recommend reaching out to a vet to rule out a potential medical cause. There are a number of conditions that can make a cat hungry all the time including worms, hyperthyroidism and diabetes. With examination and diagnostic tests, your vet can rule out medical issues and ensure that it’s only a behavioral concern.

2. Offer Them High-Quality Food
Another reason your cat might be pestering you at night might be because they still feel hungry even after eating. This can happen if you’re feeding your feline friend lower-quality food that doesn’t meet all their nutritional needs.
Their body is still screaming for those nutrients, and eating is the only way they know how to get it. Switching them to a complete and balanced high-quality diet is good for their overall health and might help you get some undisturbed shuteye in the evening.
3. Remove the Bowl After Meals
When your cat sees their food bowl, even if it’s not at mealtime, it reminds them of food. It could be that your cat is bored and has a constant visual of the food bowl, thus leading them to bug you for some extra food or snacks.
If you can keep your cat from thinking about food in the first place, you might be able to stop the begging—out of sight, out of mind, right? While this might work for your cat, it is worth noting that it’s not the most effective method out there.
4. Ignore the Begging
We know that this can be challenging. The incessant meowing, pawing at you, and those adorable, pleading eyes can be all but impossible to ignore. But we promise that if you give in, it’s only going to be more challenging to stop the behavior in the future. Every time your cat begs and you eventually give them more food, you’re just reinforcing the behavior, meaning they’re going to do it again and again.
5. Keep Them Away From You While You’re Sleeping
Your cat can’t beg if they can’t get to you! While you might enjoy having your cat in your room at night, there are numerous benefits to having a cat-free space to sleep. You also might have to deal with a cat purring and pawing at your door, but often, if you ignore it for a night or two, this behavior will stop and you won’t have to deal with begging at night anymore.

6. Give Them a Food Puzzle
This might help stop your cat from begging, or it might make it worse. Giving your cat a food puzzle helps meet their mental and physical needs while slowing down how fast they get their food, which can help keep them from begging. The problem is that once the food puzzle is empty, they might have a whole new reason to pester you. If boredom is the issue, this one might work well.
7. Ensure They’re Eating Enough
Every cat requires a different amount of food depending on their breed, size, activity levels, and any existing health conditions, and if your cat thinks they aren’t getting enough food, you can be sure that they’re going to let you know about it. But before you dive in too hard with trying to get them to knock off the begging, ensure they’re getting enough food to begin with.
While most people follow the feeding guidelines on the food’s packaging, you should also take a look at their weight and how much they’re moving during the day, and talk to your vet about how much they should eat. The problem could simply be that they need more food.
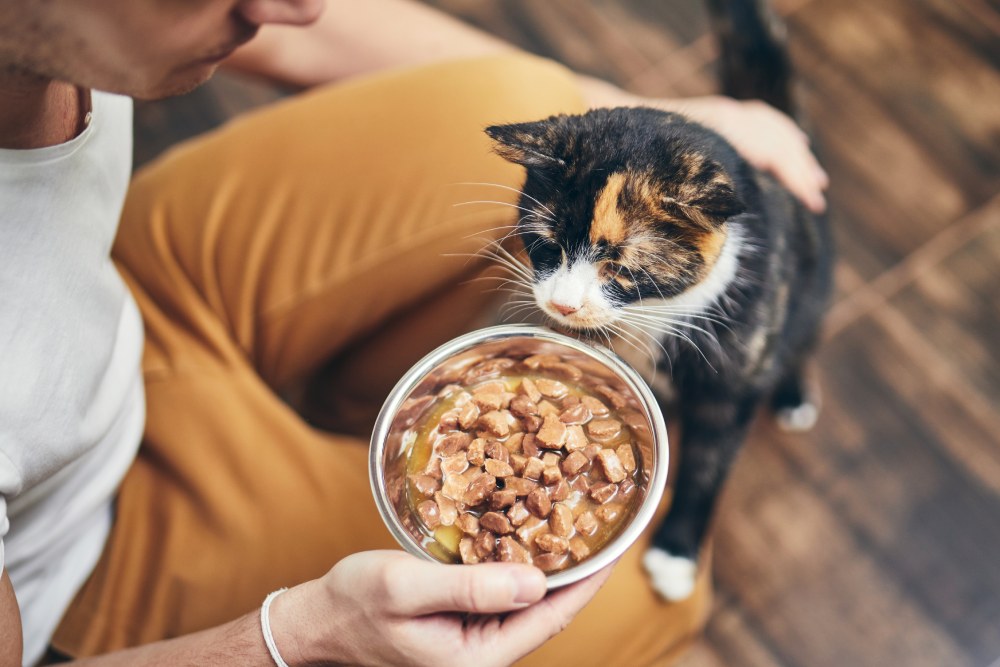

8. Offer Several Smaller Meals Throughout the Day
Cats naturally eat several smaller meals throughout the day so if your cat is trying to tell you they’re hungry, it might be beneficial to offer three or four small meals a day rather than two. However, this does not mean you should increase their overall food intake. They need the same number of calories, just spread out into smaller, more frequent feedings.
Choosing the right food and water bowls for our feline companions can pose certain challenges for pet owners. After careful consideration and research, we have found a bowl that we cannot recommend highly enough! The Hepper NomNom Cat Bowl provides a chic and innovative solution that supports cat-specific needs, such as shallow bowls and a subtle elevation that fosters whisker relief and posture comfort, as well as improves digestion.
It features an elegant contemporary design with a wide wrap-around tray aimed at minimizing any messes from ending up on your floor! Furthermore, this bowl is entirely dishwasher safe, so pet owners can spend more time with their cats instead of cleaning up after them. Discover why the Hepper NomNom Cat Bowl is right for both you and your kitty by clicking here. At Catster, we’ve admired Hepper for many years and decided to take a controlling ownership interest so that we could benefit from the outstanding designs of this cool cat company! Our Favorite Cat Bowl
Conclusion
The more tips you can follow from our list, the better, but just keep in mind that their behavior isn’t going to change overnight. It takes time and consistency to alter a pet’s behavior, so implement as many as possible, stay consistent, and give it a few days or even a few weeks to start working. We promise it’s worth it, and in the end, your cat should stop begging for more food in the evening. But if not, it’s definitely time to schedule a trip to the vet.
Featured Image Credit: Andriy Blokhin, Shutterstock
Contents
- The 8 Tips to Get My Cat to Stop Begging for Food at Night
- 1. Go to the Vet
- 2. Offer Them High-Quality Food
- 3. Remove the Bowl After Meals
- 4. Ignore the Begging
- 5. Keep Them Away From You While You’re Sleeping
- 6. Give Them a Food Puzzle
- 7. Ensure They’re Eating Enough
- 8. Offer Several Smaller Meals Throughout the Day
- Conclusion