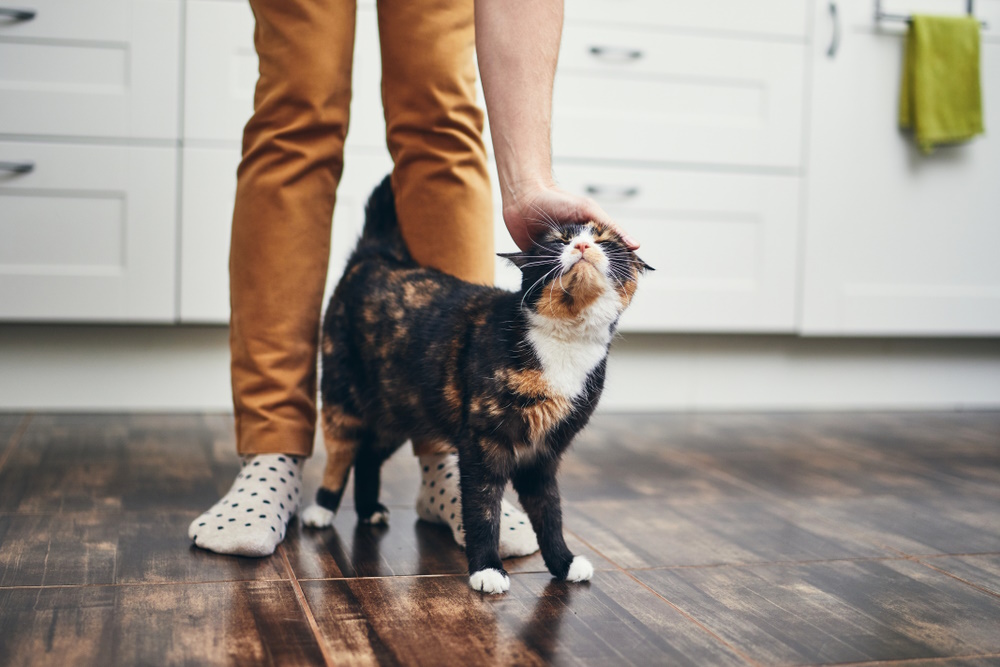
Many cat parents describe their companions as having dog-like qualities. It’s a way of saying that cats are loving, loyal, devoted, and interested in interacting with people.
There are a few activities dog-like cats engage in, including talking to their owners, acting like watch cats, defending loved ones, following people around, begging for treats and human food, cuddling with dogs, enjoying baths, and even learning commands, playing games, and taking walks.
While these behaviors may appear particularly dog-like, they’re natural for cats. Keep reading to learn more about these activities and why cats have perfectly good reasons for engaging in them.
The 10 Ways Cats Act Like Dogs
1. Participating in Conversations
Cats can produce a range of vocalizations, including hisses, purrs, and meows, the latter of which adults largely reserve for communicating with humans. To relay information to each other, cats use body language and scent, which humans aren’t very good at picking up on.
Over time, cats have learned that meowing is the best way to get messages across to people. While some are relatively quiet, there are also those who relish having conversations with their favorite people and happily meowing to ask for things.

2. Behaving like Watchcats
Cats sometimes sit in front of doors and appear to be keeping watch. Cats are territorial creatures who generally feel most comfortable in familiar environments and like to ensure their domains stay to their liking, which often includes keeping an eye on who comes and goes.
3. Coming to the Defense of Loved Ones
Cats truly love their people and come to their rescue in all sorts of ways, which makes sense since they form bonds with their owners that resemble those that exist between parents and babies.
Cats have been known to wake sleeping humans to warn them of fires. They’ve kept kids from falling down stairs and even saved lives! One truly handsome boy named Fluffy retrieved a cell phone so his elderly human (who had fallen) could call for help.

4. Keeping People Company
Although there are some cats who prefer to be by themselves, many are affectionate. Feral cats frequently live in colonies with other cats and enjoy doing so as long as there’s enough food around.
Male kittens usually end up moving away, but it’s relatively common to find several generations of female cats living together in feral colonies. Keeping people company meets indoor cats’ social needs and can provide fun and mental stimulation.
5. Asking for Treats and Human Food
While pet parents often associate begging with dogs, it’s a well-known feline pastime as well. Cats can become persistent when it comes to begging for treats and human food.
Cats are attracted to most human food, but it’s better for cats to avoid it since eating too much can lead to obesity, and consuming meals with toxic ingredients (like onions and garlic) can result in trips to the emergency veterinarian.

6. Snuggling With Dogs
Some cats prefer companionship, and it makes perfect sense for those who enjoy hanging out with well-behaved and socialized dogs who treat them like family. Cats who grow up with dogs are quite comfortable around them and happy to include them in their inner circles.
When kittens are exposed to sweet, friendly, well-behaved dogs, they’re more likely to grow into adults who enjoy having canine friends.
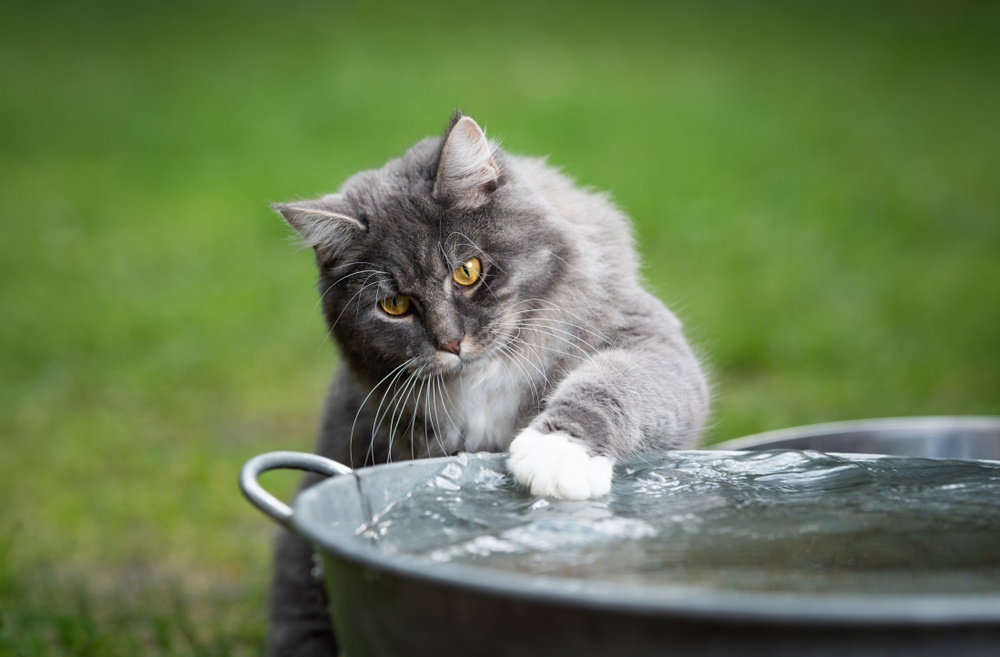
7. Liking Water
Although most cats don’t like water, some can’t get enough of it. Water-loving cats sometimes bat at the water dripping from faucets and stare at it as it swirls down drains, but there are also ones who enjoy a good swim.
Bengal, Savannah, Maine Coon, and Turkish Van cats, to name a few, often love water.

8. Mastering Commands
While cats are thought of as being untrainable, many are willing to learn “commands” under the right circumstances. Cats thrive when they have lots of mentally stimulating activities, and learning commands fits the bill for many.
Cats are capable of learning to come when called, shake hands, sit, and stay as long as it’s worth the effort. Clicker training works well with cats, as it makes it super easy for them to connect verbal commands with the action they’re being asked to complete.
9. Walking on Leashes
Fresh air and exercise are both great for cats, and many enjoy exploring the great outdoors during leashed and supervised walks.
Leashed walks provide mental stimulation, physical activity, human-cat bonding time, and fun, and it makes sense that many cats look forward to them.
The best cat leashes are sturdy, comfortable to hold, and easy to attach to the harness. Hepper's Cat Harness & Leash Set offers all that and more, which is why we highly recommend it.
This set includes a lightweight velvet and mesh harness with reinforced stitching, quick-release buckles, and reflective strips, plus a five-foot leash made from sturdy nylon climbing rope. We especially love this leash's rotating clamp and padded neoprene handle. At Catster, we’ve admired Hepper for many years and decided to take a controlling ownership interest so that we could benefit from the outstanding designs of this cool cat company!
10. Playing Games
Cats can pretty easily learn to play games like fetch. Positive reinforcement, patience, a few treats, and lots of praise are all that’s needed. Cats can also learn to do some really amazing things, like running agility courses.
The Cat Fanciers Association even has organized agility competitions for cats that moggies do quite well in! Short, positive training sessions are almost always the best way to motivate feline cooperation.
Conclusion
Although there are independent cats that aren’t interested in interacting with people, others don’t like being away from their owners for a second. When cats are deeply bonded with their owners, they’re often described as dog-like. They frequently follow people around, beg for food, and enjoy going on leashed walks.
Featured Image Credit: Jaromir Chalabala, Shutterstock