If your cat has ever had fleas, you’ll know what a pain it is to get rid of them. Trying to find the right method to get rid of fleas while avoiding poisonous pesticides is no joke! And if it’s a wet time of year, you might wonder whether the rain would help kill fleas or make it worse. The truth is, it’s hard to tell. Rain has some positive and some negative effects on fleas.
In general, rain can kill fleas in some situations, but it can also give them what they need to grow stronger and breed faster. Fleas thrive in humid places, but too much rain can hurt flea populations as well.
Hardy Fleas
There’s no doubt about it—fleas are hard to kill! If it were easy to get rid of fleas, chemical dips, and treatments wouldn’t be so popular. So, it’s no surprise that a little rain (or even a bath) won’t kill the fleas hanging out in your pet’s fur. In fact, fleas can survive being submerged in water for up to 48 hours! That’s why soaking your pet isn’t enough to get rid of adult fleas.
But flea eggs are much more vulnerable—they can be washed away or killed if there’s too much water. And since flea eggs are often deposited in the soil, heavy rainfall can be dangerous. But fleas thrive in damp soil and humid air. That means that as long as the flea eggs are relatively protected, rain can be good for fleas, not bad.
 Flea Life Cycle
Flea Life Cycle
Egg
Fleas start out as eggs. These eggs can be laid on your pet’s fur or in the soil. The egg stage is the most vulnerable time for fleas. During heavy rainfall, soil can be inundated with water, drowning the eggs, or it can be washed away, destroying any eggs.
Larvae
When fleas hatch into larvae, they are very vulnerable to changes in humidity. In low-humidity environments, they can dry up and die. In general, the higher the humidity, the faster flea larvae grow. They can take in moisture from the air in humid environments, helping them stay strong and healthy. However, extremely high humidity (above 95%) can be bad for flea larvae.
However, like eggs, larvae can be vulnerable to heavy rains. They can be drowned or washed away in the right conditions. They also need to feed on the feces of adult fleas. If their food source is washed away, larvae might starve.
Adults
Adult fleas are very hardy and mobile, making it unlikely that heavy rains will harm them. They are likely to find higher ground or a furry host if it is raining too hard, and they can survive being submerged for much longer than juvenile fleas.
 Dealing with Fleas
Dealing with Fleas
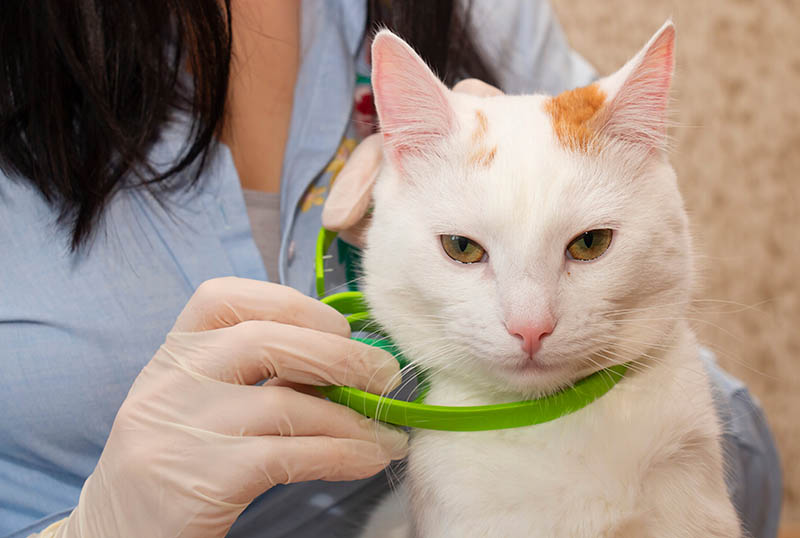
Cats need flea protection in wet and dry weather. There are lots of different ways to protect your home and cat from fleas. Flea collars can reduce the chances that a flea picks your cat as a host. Sprays can kill fleas around your home and yard. Topical treatments are applied to your cat’s fur to prevent or kill fleas. Oral treatments can be given to your cat on a monthly basis to stop fleas from infesting your cat.
One treatment that doesn’t work well in wet weather is diatomaceous earth. This silica-heavy mineral is a great way to kill fleas by desiccation—pulling water out of their bodies—without adding any pesticides to your home. But since it only works when dry, it’s not an ideal solution in humid or rainy environments.

Last Thoughts
If you’ve got a cat, don’t expect heavy rain to protect it. Although rainfall can kill fleas in some situations, it can also give them everything they need to grow stronger and breed faster. Instead, it’s important to have a solid science-backed plan to help your kitties stay flea-free. No matter what option you prefer, make sure your cat is protected year-round, no matter the weather.
See also:
- Does Cold Weather Kill Fleas on Cats? (Vet Approved Advice)
- Does UV Light Kill Fleas on Cats? Vet Reviewed Treatment Options
Featured Image Credit: BrittanyNY, Shutterstock




 Flea Life Cycle
Flea Life Cycle Dealing with Fleas
Dealing with Fleas






