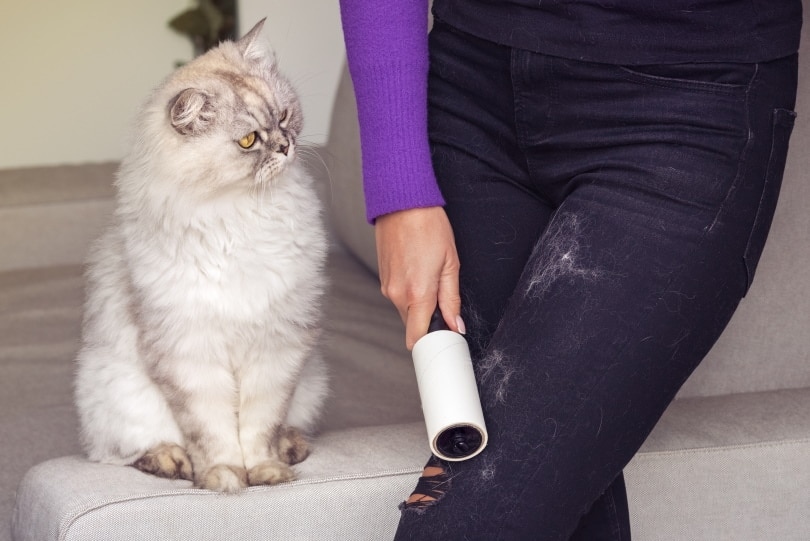
As much as we love our cats, the same cannot be said about the tiny sticky hairs always present on clothes, furniture, and bedding. But it is the price we must pay for the comfort, joy, and companionship these little furry pets bring.
The good news is that you can get rid of cat hair from your surfaces. With the best cat hair remover tool at hand, you are on your way to a fur-free lifestyle. These tools come in different shapes and sizes, including rollers, brushes, gloves, de-shedders, and vacuum cleaners. But how can you find the best remover tool?
Here are 10 of the best cat hair remover tools based on extensive research, reviews, and expert testing. These remover tools will keep pet hair away from your belongings.
A Quick Comparison of Our Winners in 2024
| Image | Product | Details | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Best Overall |

|
ChomChom Roller Pet Hair Remover |
|
CHECK PRICE |
| Best Value |

|
Fur-Zoff Pet Hair Removal Tool |
|
CHECK PRICE |
| Premium Choice |

|
Bissell Pet Hair Eraser Vacuum |
|
CHECK PRICE |

|
Smart Sheep Wool Dryer Balls |
|
CHECK PRICE | |

|
Brellavi Pet Hair Remover |
|
CHECK PRICE |
The 10 Best Cat Hair Remover Tools
1. ChomChom Roller Pet Hair Remover – Best Overall

| Material | Plastic |
| Suitability | Furniture, Car Seats, Bedding |
| Type | Roller |
Chomchom is a trustworthy brand that offers you an easy and efficient way to remove cat hair. The ChomChom Roller Pet Hair Remover does not use an adhesive. Instead, when you move it back and forth, it creates static electricity that attracts pet hair.
The Chomchom Roller collects the cat hair in an easy-to-clean compartment. You only need to open the compartment and empty its contents. This design saves you money on replacements and refills.
We recommend the Chomchom roller as the best overall cat hair remover because it can withstand everyday use. In addition, it is functional since you can brush in either direction or on any surface.
- Removes pet hair fast
- No batteries required
- Eco-friendly design
- Features a hair-collecting compartment
- No refills
- Requires manual emptying of pet hair
- Not travel-friendly
2. Fur-Zoff Pet Hair Removal Tool – Best Value

| Material | Recycled Materials |
| Suitability | Car seats, Carpets, Couches, Clothing |
| Type | Sponge |
Fur-Zoff Remover Tool is a handheld sponge that works like magic in attracting pet hair. This remover is made from 90% foamed recycled glass and easily removes cat hair from bedding, furniture, carpets, clothing, and car interiors.
The sponge works faster and more effectively than sticky rollers, rubber tools, and vacuums. A light sweeping motion allows the sponge’s hair-scaled texture to clean pet hair from surfaces quickly and easily.
This Fur-Zoff remover is hypoallergenic, odor-free, and made in the USA. In addition, it is cost-effective as it needs no electricity and does not wear out. We recommend it as the best cat hair remover tool for the money.
- Hypoallergenic and odor-free
- Uses no electricity
- Ideal for carpets, couches, and car seats
- Effective
- May scratch hard surfaces
3. Bissell Pet Hair Eraser Hand Vacuum – Premium Choice

| Suitability | Upholstery, Stairs, Carpet |
| Type | Handheld Vacuum |
Turn to this handheld vacuum to remove cat hairs from the carpet and upholstery you didn’t know were trapped. Bissell Pet Hair Eraser Hand Vacuum is equipped with a 14V lithium-ion battery for extended runtime while cleaning. Its motorized brush removes pet hair, embedded dirt, and various pet messes.
The vacuum includes a set of specialized tools for cleaning multiple surfaces. The upholstery tool attracts pet hair from furniture and soft surfaces as the crevice tool removes pet hair from tight and hard-to-reach areas.
This handheld vacuum features triple-level filtration to improve cleaning performance. It also comes with a 0.7-liter dirt bin that holds more dirt and is easy to empty.
- Motorized brush
- Upholstery tool
- Crevice tool
- Large dirt bin
- Triple level filtration
- Pricey
- No attachment support
4. Smart Sheep Wool Dryer Balls – Best for Kittens

| Material | Wool |
| Suitability | Laundry |
| Type | Wool Balls |
It is annoying to find your clothes still covered in kitten hair after laundry. Luckily, the Smart Sheep Wool Dryers Balls are a natural, reusable, and effective way to remove these hairs.
The balls are made from high-quality New Zealand wool and manufactured through Nepal’s ethical fair-trade practices. They are designed to last for 1,000-plus loads, and on average, people use them for 3 to 5 years.
Dryer balls are easy to use. Just toss a few in the dryer with your laundry and wait. These balls not only trap pet hair from your clothes but also decrease drying time and increase softness!
Moreover, since these wool balls are natural, they are safe for babies, people with sensitive skin, and play toys for your kittens. We recommend the Smart Sheep Wool Dryer Balls as the best kitten hair remover tool based on the above features.
- Natural
- Lasts for up to a thousand loads
- Eco friendly
- High-quality New Zealand wool
- Increases static in certain fabrics
- Suitable for laundry only
5. Brellavi Pet Hair Remover

| Material | Plastic |
| Suitability | Car Seat, Carpet, Clothing, Bedding, Fabric, Couch |
| Type | Self-Cleaning |
Tired of finding strands of your cat hair on your clothing, carpet, and couch? Get the Brevalli Pet Hair Remover.
Just one swipe and this double-sided brush removes lint, fluff, and pet hair, thanks to the dense and strong adhesive. Follow the direction of the arrow on the upper part of the handle for easy and efficient brushing.
The brush features a self-cleaning base. This eliminates the need to remove cat hair from the brush manually. Instead, you dip the brush in the self-cleaning base after use. The base collects hair from the remover brush, and it is removable for easy cleaning.
The pack also comes with a travel-sized pet brush to keep your clothes free from cat hair when traveling. This brush ensures that you no longer must shy away from dressing in your favorite colors. It easily fits in a purse or car compartment and has a self-cleaning base for easy disposal.
- Features a travel-size brush
- Self-cleaning base
- Double-sided remover
- Dense, fluffy, strong adhesive
- Breeze to use
- Pricey
- Must follow the direction of the arrow
6. Delomo Pet Hair Remover Roller

| Material | Nylon, ABS plastic |
| Suitability | Furniture, Car Seat, Carpet |
| Type | Roller |
Wouldn’t it be great to own a cat hair remover tool that cleans most of your furniture? Well, the Delomo Pet Hair Remover Roller promises to do just that.
This roller works effectively on most surfaces, including beds, pillows, sofas, quilts, carpets, and car seats. Unlike other rollers that use adhesive tape, the Delomo utilizes electrostatic absorption from back-and-forth motions to attract cat hair.
The pet hair is collected in the waste compartment for easy disposal. If you are worried about cleaning, it is pretty simple.
Press the button on the waste compartment to open it. Next, remove the pet hair for disposal. Then, clean the brush surface with a soft, wet towel because some hairs stick on it.
Save money with this reusable pet hair remover tool. With it, you get to cut costs on batteries or refills. Moreover, it is made of durable ABS plastic and will not break during use.
- Durable ABS
- Works on most surfaces
- Convenient to clean
- Reusable
- Not effective on wood, tile, and concrete
- Expensive
7. Evercare Magik Brush

| Material | Plastic |
| Suitability | Clothing, Upholstery, Bedding |
| Type | Brush |
The Evercare Magik Brush picks up everything, including lint, dust, fuzz, dandruff, and pet hair. It features double-sided red velvet bristles that catch cat hair as you swipe the brush on clothing, bedding, or upholstery. The fact that the brush is two-sided guarantees longevity and is convenient for left and right-hand users.
Due to the absence of a sticky adhesive, this brush does not pull or damage the fabric. The brush comes with a comfortable grip that makes it easy to use. It is made of durable plastic and can withstand everyday use.
The Evercare Magik brush comes in a pack of three. This way, you can have one at home, another in your car, and a third in your office drawer. These brushes will help you keep your clothing, upholstery, and car seats looking their best.
- Pack of three
- Reusable and durable
- Ideal for left and right-hand users
- Velvet bristles pick everything
- No self-cleaning base
- Larger for travel purposes
8. OXO Good Grips FurLifter Furniture Brush Lint Roller

| Material | BPA-free Plastic, Microbristles |
| Suitability | Furniture |
| Type | Self-Cleaning, Brush |
Removing pet hair feels effortless with the Oxo Good Grips Pet Hair Remover. It is a combination of a traditional brush’s effectiveness and the convenience of a self-cleaning base.
The brush has powerful FurLifter bristles that trap cat hair with a simple swipe. There is an arrow on each side of the brush to guide you in which direction to follow.
When done cleaning, dip the brush in the base. The self-cleaning base contains fibers that trap cat hair inside, leaving your brush clean. When the base is full, open the cap and remove the collected hair.
This FurLifter brush comes with a flexible handle that pivots away. It proves helpful during cleaning because it gives clearance between your hands and furniture. The handle is soft, non-slip, ergonomic, and comfortable on the hands.
- Self-cleaning base
- Flexible handle
- Effective
- No refills
- Powerful micro bristles
- Short handle
9. Pet Neat Grooming Brush

| Material | Stainless Steel |
| Suitability | Cats |
| Type | De-shedding Brush |
Rather than waiting for your cat to shed, Pet Neat Grooming Brush removes up to 95% of dead and loose hair. This saves you the headache of cleaning your floors and couches. It also saves you time and money spent on pet grooming services.
This brush is designed to withstand everyday use for years. Its 100 mm stainless steel blade has a protective cover for blade longevity and safety. The non-slip grip handle is sturdy, promises utmost precision, and is comfortable to use.
The Pet Neat Grooming brush reduces grooming time to a mere 10 minutes. During this time, you get to develop and maintain a strong bond with your kitty.
- Durable
- 4-inch rust-resistant blade
- Removes 95% of loose hair
- Easy to assemble
- Easy-grip handle
- Requires the use of other remover tools
10. Evriholder FURemover Extendable Pet Hair Removal Broom

| Material | Rubber, Plastic |
| Suitability | Carpets, Floors |
| Type | Broom |
Nothing removes messy cat hair on floors and carpets better than the Evriholder FURemover Extendable Pet Hair Removal Broom. Its bristles are 100% natural rubber, and they work like a magnet to remove pet hair from rugs, hardwood, carpets, and linoleum. Apart from floors, this tool also sweeps lint, dirt, and dust from upholstery.
This pet hair removal broom is versatile as it also features a 12-inch-long rubber squeegee edge. Flip the broom to clean windows, windshields, and showers with ease. The squeegee is efficient at wiping away messy spills on concrete, tile, carpet, and hardwood floors.
The broom comes with an easily adjustable telescopic handle. You can extend the handle length from 36 to 60 inches to access the furballs in high places.
- Built-in rubber squeegee
- Natural rubber bristles
- Adjustable telescopic handle
- Easy to clean
- Ideal for multiple surfaces
- Weak handle
- Does not grab all hairs
Buyer’s Guide: Choosing the Best Cat Hair Remover Tools
Since there are plenty of pet hair remover tools in the market, not all are worth your money. Take your time looking at the following features to find a suitable tool for your needs.
Efficiency
Mention that one area that your cat does not have access to. If your answer is none, it means you have plenty of ground to clean when it comes to removing cat hair.
Therefore, when choosing a remover tool, find one that is efficient and time-saving. Look for remover models that hold a lot of lint and demand minimal effort.
Pet remover brushes with a cleaning base or rollers with a lint bin are always a bonus. If you opt for a vacuum remover, check its bin capacity.

Features
Some cat hair remover tools do more than remove pet hair. For example, some clean up other pet messes and spills while others can clean your windows and bathrooms. If a remover tool specializes in more than just cat hair, it is worth considering it.
Durability
Naturally, you do not intend to buy a remover tool that will need replacing after a few weeks or months. Although most manufacturers may guarantee long-lasting products, it would be best to read honest customer reviews for better insight.
Moreover, find out whether it is easy to clean and maintain the cat hair remover tool. A remover brush is not efficient when it is clogged with pet hair. Self-cleaning removers, on the other hand, are convenient and durable.

Shutterstock
Price
How much are you willing to spend on the cat hair remover tool? There is no need to go broke while buying accessories. Therefore, find an affordable option that is functional, high-quality, and durable.
In addition, consider whether there are additional costs like refills and replacements. You may spend more on a reusable brush, which is cost-effective in the long term. On the other hand, you may spend less on a roller that will demand replacement rolls every few months.
Type
There are several types of pet hair removers, and it is essential that you find what’s best for you. Depending on the surfaces you need cleaning, you can opt for a roller, vacuum, brush, or dryer ball.
Rollers work through back-and-forth motions, creating static to attract pet hair. They are effective on bedding, furniture, and car seats. Vacuum cleaners are powerful and suck in pet hair, dander, dust, and various messes. You can use a vacuum cleaner on floors and upholstery.
The best cat hair remover tools for clothing are dryer balls and brushes. Dryer balls collect pet hair from the laundry. On the other hand, a brush swipe also collects any hair from your clothing and upholstery. Then there are de-shedder tools that collect pet hair before your cat sheds.
Size
To determine the best size of a cat hair remover tool, consider whether you need to clean a large area or tight spaces or one to carry with you. Small, light remover tools are best for removing pet hair on the go or in small spaces.
You will need a bigger tool if you have large surfaces to clean. A vacuum cleaner, for instance, comes with different attachments, which are perfect for cleaning different surfaces.

Cleaning
Do not forget the cleaning aspect when looking for a cat hair remover tool. Some rollers use sticky tape sheets that you rip and discard after use, while others have a dirt compartment.
Some pet hair remover brushes require you to manually remove fur from them, while others come with a self-cleaning base. Vacuums feature a dirtbag compartment that is easy to clean.
For this, consider which remover tool is easy to clean before making the purchase.
Tips to Reduce Cat Hair in Your Home
Is it possible to reduce cat hair from the furniture, floors, bedding, and clothing? Yes, and here is how to go about it.
Schedule Grooming Time
Scheduling and maintaining a grooming routine is the easiest way to reduce cat hair in your home. Doing so prevents excessive shedding and buildup of cat hair.
Invest in Appealing Areas for Your Kitty
What is common between your couch, armchair, and bed? They are all comfortable surfaces, a reason your pet is drawn to them. For this, invest in providing comfortable spaces for your cat, and cat trees are an excellent place to start.
Keep Your Cat Hydrated
When your kitty is well-hydrated, they enjoy a healthy coat. But getting your cat to drink water is easier said than done.
The easiest way to achieve this is by feeding your pet wet foods as they contain water. Alternatively, elevate the water bowl so your cat feels safe and comfortable drinking from it.

Conclusion
As a pet owner, settle for the best cat hair remover tool. It will save you time and money and keep your home looking at its best.
The Chomchom roller takes our top spot as the best cat hair remover tool. It collects deeply embedded hair with the electrostatic charge created from back-and-forth motions. This reusable tool does not require a battery source of refills.
Suppose you are looking for a versatile, functional, and effective remover tool and are willing to pay the price. In that case, we recommend the Bissell Pet Hair Hand Vacuum. It features a motorized brush tool, specialized pet tools, a large-capacity dirt bin, and triple-level filtration.
We hope this review helps you find the right tool for removing cat hair from your clothes, bedding, and upholstery.
Featured Image Credit: Daria Kulkova, Shutterstock
Contents
- A Quick Comparison of Our Winners in 2024
- The 10 Best Cat Hair Remover Tools
- 1. ChomChom Roller Pet Hair Remover – Best Overall
- 2. Fur-Zoff Pet Hair Removal Tool – Best Value
- 3. Bissell Pet Hair Eraser Hand Vacuum – Premium Choice
- 4. Smart Sheep Wool Dryer Balls – Best for Kittens
- 5. Brellavi Pet Hair Remover
- 6. Delomo Pet Hair Remover Roller
- 7. Evercare Magik Brush
- 8. OXO Good Grips FurLifter Furniture Brush Lint Roller
- 9. Pet Neat Grooming Brush
- 10. Evriholder FURemover Extendable Pet Hair Removal Broom
- Buyer’s Guide: Choosing the Best Cat Hair Remover Tools
- Tips to Reduce Cat Hair in Your Home
- Conclusion