We all love our feline friends. They keep us company and even add beauty and elegance to our houses. But there are probably a few habits that they develop over time that may be annoying to you.
One such habit might be hanging out in your flowerbed all day. This might not be such a problem if all they did was sit there, but what they perceive as relaxing and playing is actually destroying the flowers. So, why are cats so attracted to flowerbeds? What can you do to keep your kitty out of your garden?
For the answer to that, you are in the right place. Here, we give you useful tips for keeping your feline off your beloved flowers.
The 11 Ways to Keep Cats Out of Flowerbeds
1. Don’t Unintentionally Attract Cats
Believe it or not, you might be doing some things that are luring your cat or even your neighbor’s cat into your flowerbed. For instance, you might be leaving food remains in or around the area.
The scent alone is strong enough to attract your kitty. The presence of open trash cans could also be a reason that cats cannot leave your compound. You want to ensure that these are tightly closed throughout and nowhere near your garden.
Another suggestion is to clear the bushes around your house. While your cat may not be so attracted to them, the wild ones will always find some sort of shelter there. Cats have a tendency to form habits, and those bushes might become their usual hiding spots.

2. Use Unattractive Scents
There are two sides to the coin when it comes to the use of scents. We have already looked at the first one. Nice scents could be a reason that cats are not willing to leave your flowerbeds. Those include scents from cat foods and other substances.
But why not try it the other way around? This time, try using unattractive scents that they don’t like. For instance, just sprinkle some black pepper on your flowerbeds. Alternatively, try using citrus peels. Cats avoid these scents whenever possible.
Some of these may need to be replaced several times. Scents that come from black pepper or cinnamon will obviously be washed away in the event of heavy rainfall. You must remember to sprinkle more when things clear up.
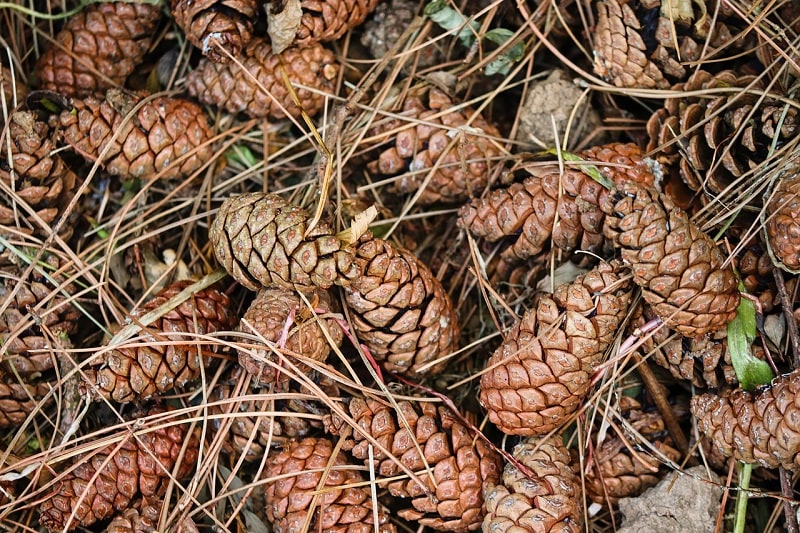
3. Create Rough Surfaces
Who doesn’t like being comfortable? Cats, like human beings, love luxury. So, attempt to strip your flowerbeds of the comfort they are surely enjoying.
One tactic you might want to employ is using rough surfaces to keep them away. For instance, find some prickly pine cones, and push them into the soil surrounding the flowerbed.
You can also try covering that entire area with some sharp twigs so your cat cannot easily walk through the area. You can be sure that this method will keep them from spending long hours dozing among your flowers.

4. Install Electric Fences
This one might sound to be a bit dangerous, but it is worth giving a shot. There are safety precautions that you can use to ensure that your feline friends will not be injured. The general expectation is that an electric fence will give a small shock to your cats when they attempt to come into contact with the bed. It also discourages them from coming back.
You can also use a wire that has a very low voltage to serve as a deterrent. To ensure that this method is effective, you should get a fence that is at least 4 inches tall.
5. Dig Barriers
It goes without saying that cats are playful creatures. They are also stubborn and destructive. Besides just invading your flower garden, they might also go on another adventure and end up ruining your plants for good.
For example, they are fond of digging into the soil to make holes that they convert into litter boxes. The good news is that there are certain measures that you can take to keep that from happening.
This includes the use of physical barriers. You want to try using something like a wooden lattice. Spread this all over your flower garden. You can then hide it from cats by covering it with mulch.
In this situation, cats will not be in a position to dig into the soil.

6. Get Rid of Plants That Cats Love
Did you know that mint and spider plants are natural cat-attracting plants? You should ensure that such plants grow as far away from your flowerbed as possible.
There are others, like catnip, valerian, and silvervine. You do not want a case where you are spending so much effort and time to keep the cats away, yet they keep coming back naturally.
- You may also like: Ways to Keep Cats Out of a Sandbox
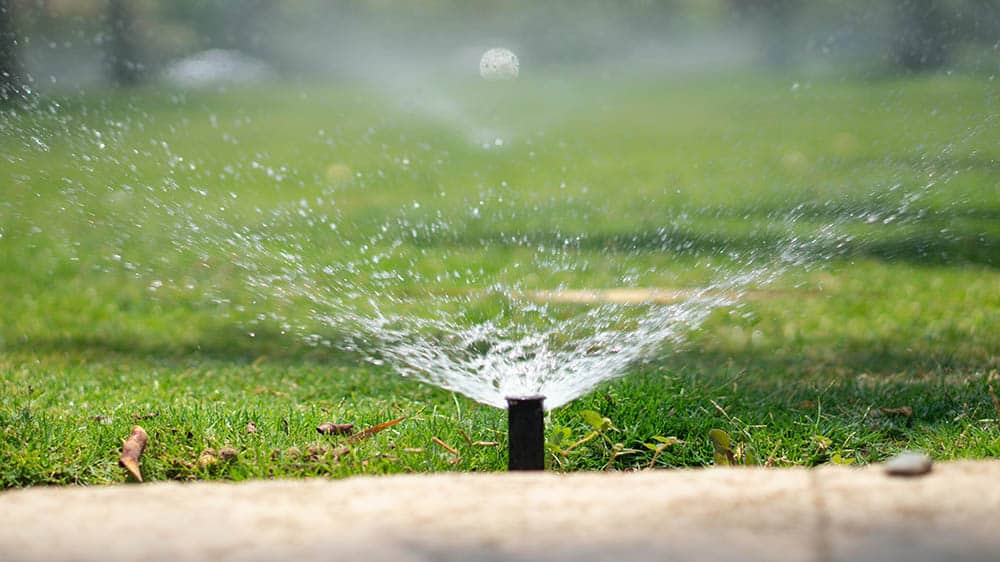
7. Use Water Sprinklers
Just like humans generally hate being rained on, so do cats. They are uncomfortable walking around when they are wet. As such, water can be used as a useful hack to keep them away from your flowerbed.
The first approach that you might want to try is using a spray bottle. Wait until your cat looks comfortable and spray them away. There is a high chance they will break the habit of camping in your flower garden.
While that can be useful, it may be tedious and quite demanding of your own time. That is why you should also try the second approach: using sprinkler systems that are activated when they sense motion. This is unlikely to lead to much wastage of water. They will also achieve the desired results.

8. Use Oscillate Fencing
This is also another creative hack that you can use to keep cats at bay. Do you already have a fence, yet it seems like it is not helping? That could be probably because the cats are jumping right over the fence and into your flower garden.
If that is the case, this approach is the best method for you. An oscillate fence is usually installed above your normal fence. How does it function? The moment the cat tries to jump over, it rolls, making it impossible to get to the other side.
No matter how much the cat tries, they will never be able to get into your flowerbed. Try this method out and see if it helps.
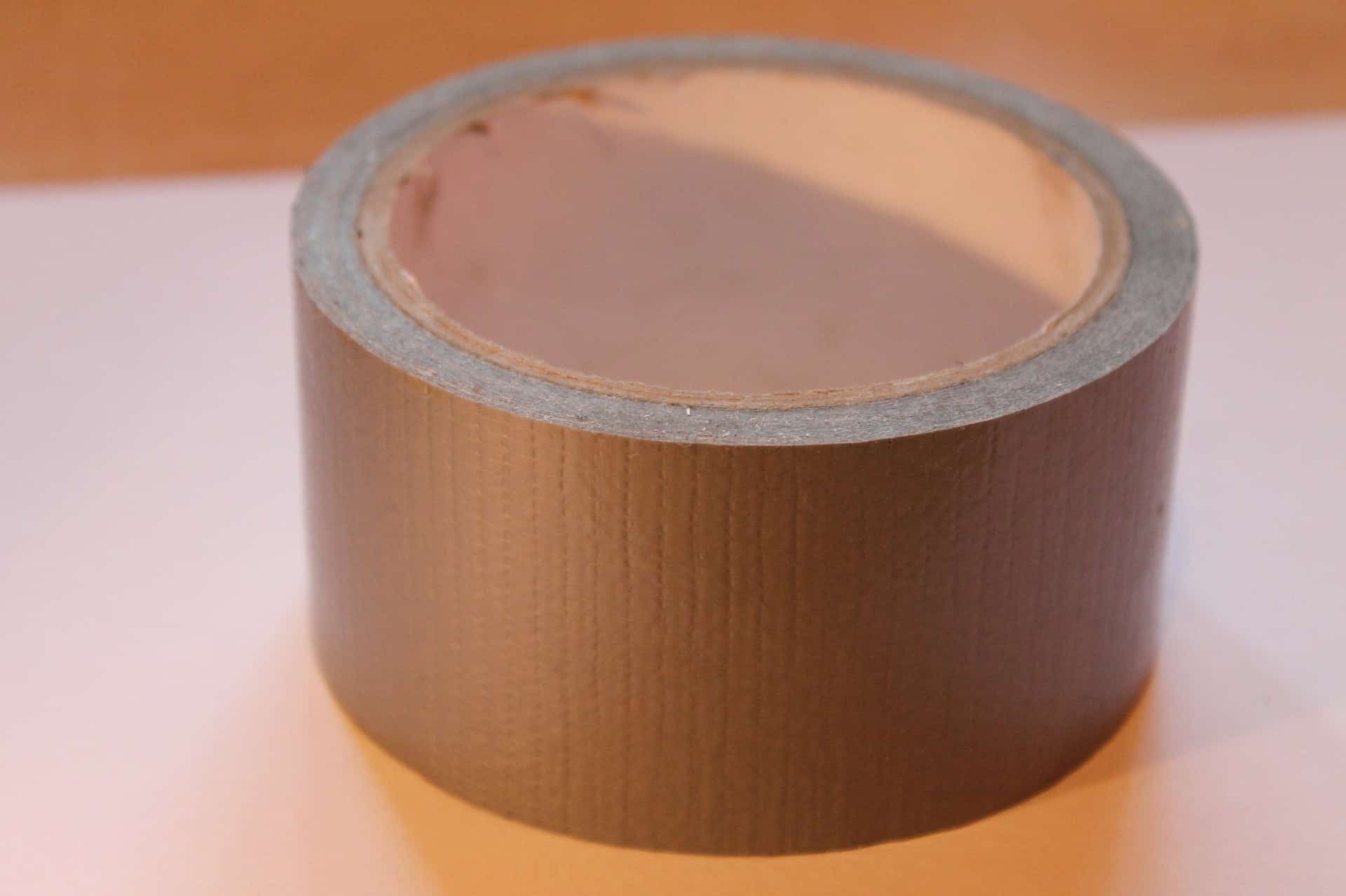
9. Use Tape as a Deterrent
You are probably wondering how tape can help keep a cat away from the flowerbed. Believe it or not, tape works like a charm when it comes to keeping cats far away. It is also a cheap means of preventing those stubborn cats from entering the garden.
The first step is to get duct tape. Just as an assurance, this is not toxic and will not harm your cat in any way. You will then proceed to make some tape balls that you will be using for the job.
You have to attach these to the beds that your feline friends have made a habit of entering. As your cat tries to jump away, the tape balls will cling to their skin, irritating them and preventing them from seeing where they can safely land.
If it happens repeatedly, the cat will learn the lesson.

10. Install Chicken Wire
Chicken wire will work the same way hard surfaces would. The main reason to use it is to prevent cats from digging holes in your garden. One advantage is that it’s easy to employ.
All you need to do is to get enough wire that can cover your entire flower garden. You then have to lay it down, allowing plants to pop up through the spaces between the mesh. While your plants will still grow perfectly, you will have posed a challenge to cats.
They may not like how hard it is to dig through the soil. It will not take long to drive them away.
11. Construct a Litter Box
One way of keeping cats out of the flower garden is by giving them a reason not to go there in the first place. As we have seen, some cats destroy your flower garden just because they want to make holes to use as litter boxes.
So, you can make them an actual litter box outside your house. For example, try using a plastic bin that is filled with sand. Chances are they will opt to relieve themselves there rather than in between flower petals.
Final Thoughts
You may have to utilize multiple methods to keep cats out of your flowerbeds. If the problem is your own kitty, consider keeping them indoors and constructing a catio for your house so they can still have outdoor time. For stray, feral, or neighbors’ cats, try something as simple as rough surfaces and unpleasant scents before moving onto electric fencing and sprinklers.
See also:
Featured Image Credit: Gundula Vogel, Pixabay
Contents
- The 11 Ways to Keep Cats Out of Flowerbeds
- 1. Don’t Unintentionally Attract Cats
- 2. Use Unattractive Scents
- 3. Create Rough Surfaces
- 4. Install Electric Fences
- 5. Dig Barriers
- 6. Get Rid of Plants That Cats Love
- 7. Use Water Sprinklers
- 8. Use Oscillate Fencing
- 9. Use Tape as a Deterrent
- 10. Install Chicken Wire
- 11. Construct a Litter Box
- Final Thoughts